Systematic Evaluation and Meta-analysis of Traditional Chinese Medicine in the Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy
Published Online: Mar 17, 2025
Received: Oct 12, 2024
Accepted: Jan 31, 2025
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/amns-2025-0211
Keywords
© 2025 Xu Huang et al., published by Sciendo
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is one of the common chronic microvascular complications of diabetes mellitus and has become the leading cause of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and its resulting end-stage renal disease (ESRD) worldwide. Although a large number of clinical studies have confirmed that timely intervention measures such as strict control of blood glucose, blood pressure, and blood lipids, and improvement of microcirculation in the early stage of DN [1-4] can delay the progression of the disease to a certain extent, so far, modern medicine still lacks targeted drugs that can effectively stop the process of renal damage in DN. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has a rich clinical accumulation in the treatment of DN, and the clinical effect is remarkable [5-8].
At present, modern medicine for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy to control blood glucose and blood pressure is the main, traditional Chinese medicine treatment of diabetic nephropathy has its unique advantages, can significantly improve the clinical symptoms of patients, delay the process of diabetic nephropathy [9-11], and the price of the drug is relatively low, the side effects of the drug is small, easy for patients to take for a long period of time, the external therapeutic method of operation is simple, easy for patients to self-treatment, the medicines and food are the same source of the more convenient for patients to adhere to the long-term regulation of the patient. The external treatment method is simple and easy for patients’ self-treatment. However, there are still many problems to be solved, such as the therapeutic mechanism is not clear, the clinical efficacy needs to be verified, and the prescription needs to be further optimized [12-15]. Therefore, in-depth research on the therapeutic effects of Chinese medicine on diabetic nephropathy, exploring its mechanism and improving the level of clinical application are of great significance in improving the quality of life and prolonging the life span of patients with diabetic nephropathy [16-18].
In this paper, the protein composition is used as a starting point for the etiologic and pathological study of early DKD. Four types of TCM treatments are proposed: dialectical typing, staged typing, dialectical new use and treatment with single herbs and their extracts. The RCT of DN treated with TCM was used as the type of study. A controlled experiment was established in which the treatment group was intervened with TCM techniques such as herbs and pCms, while the control group was treated with placebo or ACEI/ARB drugs alone. Meta-analysis was utilized to analyze the results of the impact on outcome indicators such as UAER, SCr, and BUN. The risk of TCM in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy was assessed by combining adverse effects and incorporating RCT bias evaluation.
Protein is a basic substance that constitutes and maintains the life activities of the human body, and belongs to the category of “essence”, “kidney essence” and “essence” in Chinese medicine, which is biochemical by the spleen and sequestered by the kidneys. Diabetic patients with persistent microalbuminuria is an important indicator of early DKD, early DKD belongs to the Chinese medicine “thirst”, “urinary turbidity”, “essence leakage”, “edema”, “water retention”, and so on. “Edema” and other categories. Combined with the ancient Chinese medical texts and through clinical observation, modern medical doctors have gained a deeper understanding of the etiology and pathogenesis of early DKD.
In conclusion, the etiology of early DKD is mostly congenital endowment insufficiency, acquired dietary disorders, seven emotional disorders, excessive labor, vegetative yin deficiency, mismanagement and misuse of treatment, etc., and the nature of the disease is the deficiency of the original standard and the mixture of the real and the virtual and the real, with qi and yin deficiencies and deficiencies as the original, phlegm and dampness, turbid toxins, and stasis of blood as the target, and the dampness and stasis of the inter-conjugation and the prolonged period of time, which finally leads to qi, blood, yin, and yang are all deficient [19].
The Chinese Society of Traditional Chinese Medicine has issued the “Guidelines for Prevention and Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy in Traditional Chinese Medicine”, in which diabetic nephropathy is divided into main evidence, part-evidence and changeable evidence, in which the main evidence is deficiency of qi and yin, deficiency of yin in liver and kidney, deficiency of qi and blood, deficiency of yang in spleen and kidney, respectively, the main evidence is used to use the Senqi Dihuang Tang with addition or subtraction, Qiji Chrysanthemum Dihuang Pill with addition or subtraction, Danggui Blood Replenishing Tang with Kidney Qi-wan with addition or subtraction, Pianzi Lizhong Wan with Zhenwu Tang with addition or subtraction. For blood stasis, dampness-heat and phlegm-drinking, in addition to the main formula, add peach kernel, safflower and danshen to activate blood circulation and eliminate blood stasis; for dampness-heat, add Huanglian, Poria and rhubarb to clear away heat and promote dampness; for phlegm-drinking, add ErChen Tang or WuLingShan to add or subtract. Variations of the syndrome are turbid toxin violating the stomach, drowning toxin in the brain, watery qi lingering in the heart, turbid toxin stasis, all of which are caused by the pathological products of renal deficiency and powerlessness.
In the “Diabetic Nephropathy Combined Diagnosis and Treatment Guidelines” issued by the Chinese and Western Medicine Association of Chinese Physicians Association in 2021, the degree of proteinuria is graded by the degree of urine turbidity for typing and treatment. Mild proteinuria (0.5g ≤ UTP ≤ 1g in 24h urine) is accompanied by bitter taste in mouth and dryness in mouth, and the urine is red and astringent, which belongs to the injection of dampness and heat, and treatment is to use Cheng’s Dioscoreopsis Dioxide Drink with subtractions. Moderate proteinuria (1g < UTP ≤ 3.5g) with abdominal distension, fatigue, is a deficiency of the spleen and qi trap, the treatment should be used to replenish the middle and benefit qi soup, severe proteinuria (UTP ≥ 3.5g) and accompanied by dizziness, tinnitus, lumbar and knee soreness and weakness, is the evidence of renal qi is not solid, this time, we need to pay attention to differentiate between the yin and yang bias, bias Yin, it is appropriate to Zhi Bo Dihuang Tang combined with the Er Zhi Pill plus or minus, and biased in yang, it is appropriate to antler antlers to replenish the astringent Pill plus or minus.
Diabetic nephropathy prevention and treatment guidelines for Chinese medicine will be diabetic nephropathy staging and evolution of the law is summarized as the onset of the early stage, the progression of lesions, lesions, early due to diabetes mellitus for a long period of time caused by qi and yin deficiency gradually to the liver and kidney due to the kidney qi deficiency, opening and closing of the loss, open and close the less frequent urination, open and close the less and close the less urinary edema. In the advanced stage of the disease, the deficiency is more serious, mainly due to the deficiency of spleen and kidney yang, water and dampness retention, overflowing skin, and yang deficiency can not warm the four end, then cold limbs. In the advanced stage of the disease, the change of the evidence is mainly bee rise, the water and drink Lingxin shot lungs, turbid evil congestion Sanjiao, to the upper and lower grid refusal, or even drowning poison human brain.
As one of the commonly used formulas for DKD treatment, Ginseng Astragali Di Huang Tang is a basic treatment plan, which is made up of the scripture Six-flavored Dihuang Pill with the addition of Astragalus and Radix et Rhizoma Ginseng to the original formula, and changed into Ginseng Astragali Di Huang Tang to make it have the effect of double tonicity of qi and yin.
Tonifying Yang and Returning Five Soup is a blood-regulating agent, which is mainly used for treating qi deficiency and blood stasis, and has the effect of tonifying qi, activating blood and clearing collaterals, so it is commonly used in the clinic for the evidence of qi deficiency and blood stasis in stroke disease. However, as the main cause of diabetic nephropathy has been recognized by many people as qi deficiency and blood stasis, therefore, following the viewpoint of Chinese medicine of treating different diseases with the same treatment, Tonifying Yang and Returning Five Soup is newly used in diabetic nephropathy, and has achieved better therapeutic effect.
Kidney Energy Pill is from the “Essentials of the Golden Chamber”, in which the diagnosis and treatment of DKD have been documented, such as “a man with thirst, urinating too much, drinking a bucket, urinating a bucket, Kidney Energy Pill is in charge of it”, all of which are in line with the clinical manifestations of DKD. Kidney Energy Pill has unique efficacy in its diagnosis and treatment, which strengthens the spleen, warms the kidney, nourishes yin and helps yang, tonifies the kidney with laxative, and opens up the kidney, which is the ancestor of tonifying the kidney, and therefore it is the most suitable treatment for diabetic nephropathy with deficiency of yang in spleen and kidney with edema.
Ge Gen Scutellaria Lian Lian Tang is one of the classic ancient formulas, which is from the chapter of Sun Disease in the Treatise on Typhoid Fever, mainly used for treating diarrhea caused by heat and epidemiological evils, and its scope of application has been enlarged in the later generations. Combining the research of traditional Chinese medicine prescription with my own clinical experience, I have used it in the treatment of diabetes mellitus with the guiding principle of “treating different diseases with the same treatment” in Chinese medicine theory, and have achieved remarkable clinical efficacy.Diabetic nephropathy is one of the complications of diabetes mellitus, and its etiologic regression is inextricably linked to diabetes mellitus, and there have been its relevant studies on diabetic nephropathy.
Diabetic nephropathy is characterized by proteinuria, generalized weakness, and edema in the late stage [20]. In Chinese medicine, the pathogenesis of the disease is that the kidney qi is weak and has no power to regulate, leading to the leakage of essence and micro-substances, and Astragalus is “the most qi tonic medicine”, and its sweet and warm nature also helps to transform the qi effect of yang. Thirsty kidney disease patients are often accompanied by symptoms of edema, and astragalus has the function of diuresis and swelling, can play the role of assisting the spleen to transport water and dampness, through the channels to facilitate the waterway, improve the role of fluid dispersion, in modern pharmacology, astragalus contains astragali saponin, there is protection of the inner wall of the blood vessels, which can restore the function of microvessels in the glomerulus, thus strengthening the filtration of urinary protein to improve the patient’s renal function, and to slow down the development of the disease.The frequency of the use of yam is second only to astragalus, yam is sweet and flat, can supplement the lungs, spleen and kidneys of the three organs of the qi, but also need to medicinal drugs on the patient’s body almost no negative impact, and yam has a tonic kidney filling essence, astringent and diarrhea stopping function, can be nourished in the innate qi, fill the essence of the innate, fixing the essence of the subtle to prevent the leakage of the body. The polysaccharide in yam can significantly reduce blood glucose in the body, as well as urea nitrogen and creatinine in the blood, which can effectively alleviate some of the inflammatory reactions caused by diabetic nephropathy and protect the organs of the body. Poria, the holy medicine of dehumidification, Qing tonic good, sweet and bland in nature, with the spleen and kidney, diuresis and seepage of dampness, and thirst disease nephropathy patients with weak spleen and qi, for the dampness of the evil trapped, the earth can not be weak to cure water, so the water and dampness gathered into edema.Poria is good at tonifying qi and promoting water circulation, strengthening the spleen and seeping dampness, which can effectively reduce the symptoms of edema without harming the fluid. The active ingredients in Poria are Poria polysaccharide and Poria ethanol, which can effectively treat proteinuria and edema caused by renal insufficiency, and can slow down the development of the disease towards end-stage renal failure. Danshen is bitter and slightly cold in nature, with the effect of activating blood circulation, removing blood stasis, tonifying blood and nourishing blood. In patients with thirst-quenching kidney disease, blood stasis obstructs collaterals and hinders the operation of qi, resulting in abnormal circulation of water and liquid, which is transformed into oedema, which can be seen as stagnant blood running through the whole course of the disease. Salvia divinorum can break the blood stasis and generate new blood, which not only can reduce edema caused by blood stasis, but also can prevent the symptoms of water and drink overriding the heart in the late stage of the disease of thirst-quenching nephropathy. In modern pharmacology, Salvia miltiorrhiza also has the ability to reduce capillary permeability, reduce inflammatory exudation, and achieve anti-inflammatory effect, so as to achieve the treatment of diabetic nephropathy early inflammatory reaction, and protect the kidneys.Cornus officinalis is sour and astringent and warm in nature, with the effect of tonifying the kidney and filling in the essence, astringent and solidifying the kidney, it can supplement the kidney qi and astringent essence and micro-substances and thus protect the organs. In modern pharmacology, Cornus officinalis has obvious hypoglycemic effect and is one of the main medicines for the treatment of diabetes.
In modern research, Astragalus has outstanding therapeutic effect on DKD, as a commonly used additive and subtractive drug in diabetes mellitus and diabetic nephropathy Chinese formula. Its main active substances are astragali polysaccharides, astragali saponins and flavonoids, which can effectively improve the symptoms of DKD, and its mechanism of action may be related to the inhibition of PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 signaling pathway, increase the autophagy activity of renal tissue cells, reduce the damage of renal tissue, thus slowing down the development process of DKD. And some related studies have shown that the combined application of Astragalus injection in the conventional treatment of DKD can play a synergistic role and improve the therapeutic effect, which has a better effect on reducing proteinuria, regulating microcirculation, lowering blood lipids, and improving the renal function of patients, and it is one of the ideal methods to effectively prevent and delay the progression of DKD.The Chinese medicine Cordyceps sinensis is a well-known medicinal fungus in China, which belongs to Cordyceps sinensis of the ergot family, and has the effects of preserving the lungs and benefiting the kidneys, replenishing the deficiency and filling the essence. Clinically, it has significant anti-fibrosis, immune regulation, antioxidant, hypoglycemic and other effects, and has a better clinical protective effect on the lungs, kidneys, immune system and so on. In clinical research we found that on the basis of conventional treatment, the addition of Cordyceps preparation can reduce the excretion of urinary micro-protein in DKD patients, reduce the interstitial damage of renal tubules in DKD patients, and delay the progression of renal fibrosis. A medicinal fungus similar to Cordyceps sinensis, Cicadellia sinensis, is also getting more and more clinical attention.
RCTs of Chinese medicine for DN, with or without blinding.
For patients diagnosed with DN, the diagnosis of DN was referred to the DN diagnostic criteria piloted by the Nephrology Branch of the Chinese Society of Traditional Chinese Medicine in 2007.
Along with the basic treatment, the treatment group was intervened with TCM techniques including Chinese herbs, proprietary Chinese medicines, TCM extracts, and TCM injections, with or without ACEI/ARB drugs. The control group was treated with placebo or ACEI/ARB drugs alone, with unlimited dosage and duration of administration.
Clinical efficacy, urinary microalbumin excretion rate (UAER), blood creatinine (SCr), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), fasting blood glucose (FBG), postprandial 2h blood glucose (2hPG), cholesterol (TC), and triglycerides (TG) [21].
(1) Duplicate publications, and (2) literature with incomplete data information or questionable data.
We searched PubMed, China Knowledge Network Database (CNKI), Wanfang Data Knowledge Service, and Wipro to collect relevant RCTs of Chinese medicine interventions in DN, and the search period was set as January 2006-October 2023.The search was conducted by combining free words and subject terms, and the search strategy was adjusted according to the characteristics of different databases in a timely manner for multiple searches, to improve the search rate. The search terms included: diabetic nephropathy, traditional Chinese medicine, traditional Chinese medicine, Chinese herbal medicine, Chinese medicine, randomized controlled, clinical research.
Two evaluators independently cross-checked, and in case of disagreement, discussed or consulted with a third party to reach agreement. The extraction of basic information mainly included: (1) the basic information of the included literature, such as the title, the first author, and the time of publication. (2) Baseline characteristics of the study population, including sample size, age, gender, etc. of each group. (3) Specific details of the interventions, including the type of drug administered, the dose of drug administered, the frequency of drug administration, and the duration of treatment. (4) Key elements of risk of bias evaluation. (5) The outcome indicators and outcome measures of interest. The risk of bias of the included studies was evaluated by 2 evaluators using the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Evaluators’ Risk of Bias Assessment Tool for RCTs.
Meta-analysis was performed using RevMan 5.3 software provided by Cochrane. Relative risk (RR) was used as the effect indicator for counting data, and mean difference (MD) was used as the effect indicator for measuring data, and point estimates and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were given for each effect. Heterogeneity test was performed before combining the results (P=0.05 as the level of significance), and the magnitude of heterogeneity was quantitatively determined by combining with the I2. If there was no statistical heterogeneity among the results, a fixed-effects model was used for meta-analysis, and if there was statistical heterogeneity, a random-effects model was used for meta-analysis. The magnitude of heterogeneity was quantitatively determined. If there was no statistical heterogeneity among the results of each study, Meta-analysis was performed using a fixed-effects model. If there was statistical heterogeneity, Meta-analysis was performed using a random-effects model.
Table 1 and Figure 1 show the results of the effect of UAER, 9 studies reported UAER, 437 patients in the experimental group and 446 patients in the control group, the heterogeneity test showed that I2=94.36%, suggesting that there was a large heterogeneity among the studies. After the sensitivity analysis of each study by excluding each study, and the analysis of different subgroups of the study subjects with respect to the duration of the disease, the drug dosage form, and the evidence, the source of heterogeneity still could not be found. According to P<0.00001, I2=94.36%>50%, a randomized controlled model was chosen for the combined analysis. The meta result showed that the diamond was located on the side favoring the experimental group, SMD=-1.92, 95%CI [-2.59,-1.33], P<0.00001, the difference was statistically significant, which indicated that the experimental group was superior to the experimental group in improving UAER in diabetic nephropathy. The results showed that the experimental group was better than the experimental group in improving UAER in diabetic nephropathy. Nephropathy UAER better than the control group.
UAER affects the result
| Study or Subgroup | Experiment | Control | Std,Mean Difference | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Total | Mean | SD | Total | Weight | IV,Random,95%CI | |
| DL 2022 | 60.48 | 7.48 | 59 | 92.65 | 10.45 | 59 | 10.50% | -3.54[-4.12,-2.86] |
| TGQ 2018 | 83.64 | 14.65 | 68 | 109.56 | 16.85 | 68 | 11.49% | -1.64[-2.03,-1.28] |
| WYP 2019 | 103.45 | 16.78 | 42 | 128.17 | 15.36 | 42 | 11.26% | -1.37[-1.85,-0.95] |
| WL 2019 | 67.82 | 15.59 | 59 | 109.66 | 25.88 | 59 | 11.12% | -1.97[-2.39,-1.49] |
| WZY 2021 | 56.28 | 11.69 | 46 | 83.24 | 15.62 | 46 | 11.24% | -2.29[-2.86,-1.76] |
| ZJJ 2020 | 45.56 | 9.08 | 53 | 86.18 | 12.28 | 53 | 10.76% | -3.78[-4.21,-3.18] |
| XSH 2014 | 315.48 | 121.65 | 40 | 376.15 | 138.45 | 40 | 11.37% | -0.42[-0.81,-0.02] |
| GXY 2022 | 113.45 | 25.69 | 38 | 158.96 | 27.69 | 38 | 11.11% | -1.61[-2.36,-1.28] |
| MMK 2020 | 54.69 | 14.89 | 41 | 68.18 | 20.18 | 41 | 11.15% | -0.71[-1.26,-0.32] |
| Total [95%CI] | 446 | 446 | 100% | -1.92[-2.59,-1.33] | ||||
Heterogeneity: Tau2=0.95, Chi2=129.36, df=7(P<0.00001), I2=94.36%
Test for overall effect Z=5.69(P<0.00001).
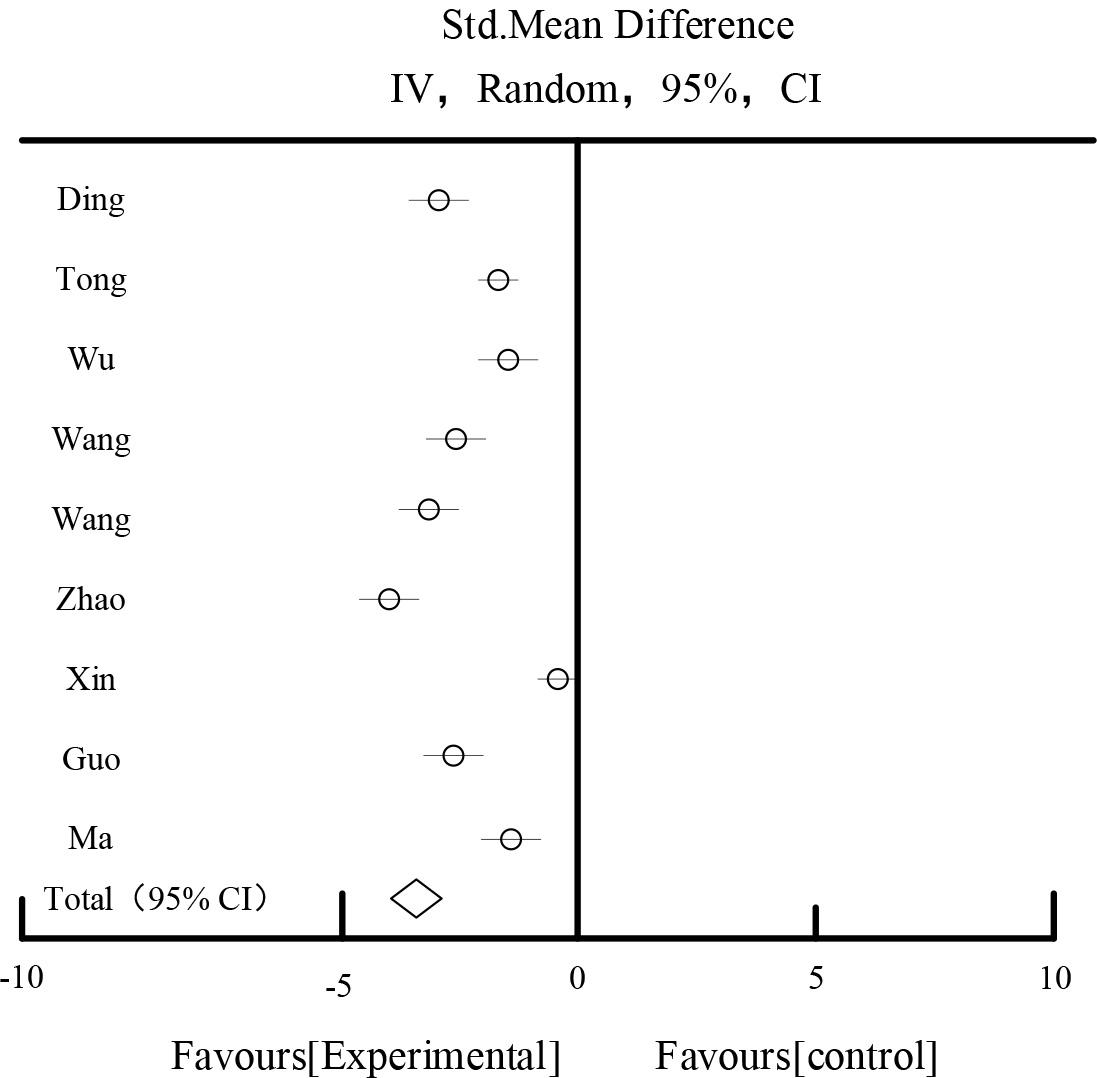
UAER affects the result
Table 2 and Figure 2 show the results of the effect of BUN. 15 studies reported 788 patients in the test group and 788 patients in the control group, and the results of the heterogeneity test showed that I2=96.85%, suggesting that there was a large heterogeneity among the studies. After the sensitivity analysis by excluding each study one by one and analyzing different subgroups of the study subjects with regard to the duration of the disease, the drug dosage form, and the diagnostic symptoms, the source of heterogeneity still could not be found. According to P<0.00001, I2=96.85%>50%, the randomized controlled model was chosen for the combined analysis. The meta result showed that the diamond was located on the side favoring the experimental group, MD=-1.78, 95C [-2.18,-1.23], P<0.00001, the difference was statistically significant, which indicated that the experimental group was better than the control group in improving the BUN in diabetic nephropathy. Better than the control group.
The effect of BUN
| Study or Subgroup | Experiment | Control | Std,Mean Difference | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Total | Mean | SD | Total | Weight | IV,Random,95%CI | |
| DL2022 | 7.15 | 1.05 | 59 | 9.76 | 1.56 | 59 | 6.26% | -2.45[-3.15,-2.36] |
| TGQ2018 | 6.21 | 0.82 | 68 | 6.21 | 0.96 | 68 | 7.26% | -0.75[-0.91,-0.42] |
| SYL2015 | 6.03 | 2.26 | 86 | 9.15 | 3.26 | 86 | 5.92% | -3.58[-4.25,-2.66] |
| WYP2019 | 3.64 | 0.41 | 42 | 5.36 | 0.52 | 42 | 7.63% | -1.95[-2.36,-1.75] |
| TCQ2021 | 10.05 | 2.46 | 45 | 11.25 | 2.26 | 45 | 5.53% | -1.15[-2.96,-0.28] |
| ZYL2022 | 7.32 | 2.02 | 62 | 10.63 | 2.06 | 62 | 6.21% | -3.15[-3.88,-2.36] |
| LQ2021 | 8.31 | 0.83 | 50 | 8.15 | 1.36 | 50 | 6.58% | -0.68[-1.02,-0.26] |
| PXQ2016 | 6.25 | 0.78 | 45 | 8 | 0.92 | 45 | 6.94% | -0.53[-0.86,-0.18] |
| WL2019 | 4.18 | 0.93 | 59 | 6.05 | 1.23 | 59 | 6.58% | -1.94[-2.36,-1.52] |
| WZY2021 | 5.92 | 0.71 | 46 | 7.55 | 0.85 | 46 | 7.63% | -2.03[-2.58,-1.76] |
| CLY2022 | 6.25 | 0.32 | 42 | 6.52 | 0.31 | 42 | 7.26% | -0.42[-0.51,-0.26] |
| JF2022 | 7.03 | 0.83 | 45 | 9.21 | 1.32 | 45 | 6.52% | -2.15[-2.68,-1.68] |
| ZXD2021 | 6.15 | 1.23 | 60 | 9.35 | 1.31 | 60 | 6.25% | -3.19[-3.58,-2.36] |
| GXY2022 | 6.25 | 0.95 | 38 | 8.15 | 1.46 | 38 | 6.25% | -1.37[-1.81,-0.86] |
| MMK2020 | 5.28 | 0.72 | 41 | 5.96 | 0.86 | 41 | 7.18% | -0.18[-0.97,-0.26] |
| Total[95%CI] | 788 | 788 | 100% | -1.78[-2.18,-1.23] | ||||
Heterogeneity: Tau2=0.83, Chi2=391.56, df=18(P<0.00001), I2=96.85%
Test for overall effect Z=6.82(P<0.00001).

The effect of BUN
Table 3 and Figure 3 show the results of SCr effects, respectively. 18 studies reported 904 patients in the Scr test group and 903 patients in the control group, and the results of the heterogeneity test showed that I2=98.56%, suggesting that there was a large degree of heterogeneity among the studies. After sensitivity analysis of each study by eliminating each study, and different subgroups of the study subjects with regard to the duration of the disease, the drug dosage form, and the symptoms of the disease, the source of the heterogeneity could not be found. According to P<0.00001, I2=98.56%>50%, the random effect model was chosen for the analysis, and the meta-analysis showed that the diamond was located on the side favoring the experimental group, MD=-15.26, 95%CI [-23.25,-8.15], P<0.0001, the difference was statistically significant, which indicated that the experimental group was superior to the experimental group in terms of improving the Scr of diabetic nephropathy. The results showed that the experimental group was better than the experimental group in terms of improving the Scr of diabetic nephropathy. Scr in diabetic nephropathy was better than the control group.
SCR impact results
| Study or Subgroup | Experiment | Control | Std,Mean Difference | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Total | Mean | SD | Total | Weight | IV,Random,95%CI | |
| DL2022 | 83.45 | 10.96 | 59 | 10.45 | 13.12 | 59 | 5.56% | -23.65[-25.65,-17.85] |
| YZX2019 | 67.15 | 12.83 | 38 | 78.26 | 10.85 | 38 | 5.56% | -6.25[-12.36,-0.75] |
| LT2016 | 138.15 | 49.15 | 35 | 142.65 | 49.66 | 34 | 3.42% | -4.15[-28.65,20.26] |
| SYL2015 | 73.63 | 15.22 | 86 | 89.25 | 19.25 | 86 | 5.86% | -15.87[-21.36,-10.52] |
| WBJ2020 | 94.25 | 6.25 | 46 | 94.15 | 6.58 | 46 | 6.26% | -0.35[-2.94,2.36] |
| WYP2019 | 62.15 | 6.58 | 42 | 67.23 | 7.26 | 42 | 6.14% | -5.25[-8.26,-1.85] |
| TCQ2021 | 123.48 | 32.45 | 45 | 142.63 | 38.15 | 45 | 4.25% | -20.35[-36.78,-4.51] |
| LQ2021 | 70.26 | 8.25 | 50 | 75.96 | 8.89 | 50 | 5.66% | -4.87[-8.57,-1.15] |
| DXM2021 | 80.27 | 8.71 | 87 | 89.52 | 9.42 | 87 | 6.15% | -9.87[-12.65,-7.05] |
| PXQ2016 | 83.58 | 13.25 | 45 | 92.56 | 19.15 | 45 | 5.70% | -8.25[-15.78,-1.41] |
| WL2019 | 50.48 | 8.16 | 59 | 64.23 | 12.36 | 59 | 5.92% | -13.48[-17.89,-10.26] |
| WZY2021 | 96.26 | 25.65 | 46 | 133.25 | 37.45 | 46 | 6.15% | -37.85[-50.26,-24.56] |
| CLY2022 | 92.88 | 4.53 | 42 | 96.15 | 3.35 | 42 | 5.48% | -4.85[-5.26,-2.14] |
| JF2022 | 152.48 | 19.85 | 45 | 187.26 | 20.53 | 45 | 4.15% | -37.89[-45.78,-28.26] |
| XSH2014 | 89.24 | 31.25 | 40 | 87.63 | 33.25 | 40 | 5.60% | 2.59[-12.85,16.58] |
| ZXD2021 | 103.21 | 13.15 | 60 | 176.12 | 14.93 | 60 | 5.52% | -70.56[-78.59,-68.52] |
| GXY2022 | 70.29 | 11.21 | 38 | 70.26 | 11.32 | 38 | 5.15% | 0.00[-5.26,5.26] |
| MMK2020 | 80.65 | 12.38 | 41 | 88.26 | 11.58 | 41 | 7.47% | -7.26[-12.69,-2.48] |
| Total[95%CI] | 904 | 903 | 100% | -15.26[-23.25,-8.15] | ||||
Heterogeneity: Tau2=197.15, Chi2=736.15, df=16(P<0.00001), I2=98.56%
Test for overall effect Z=4.26(P<0.00001).
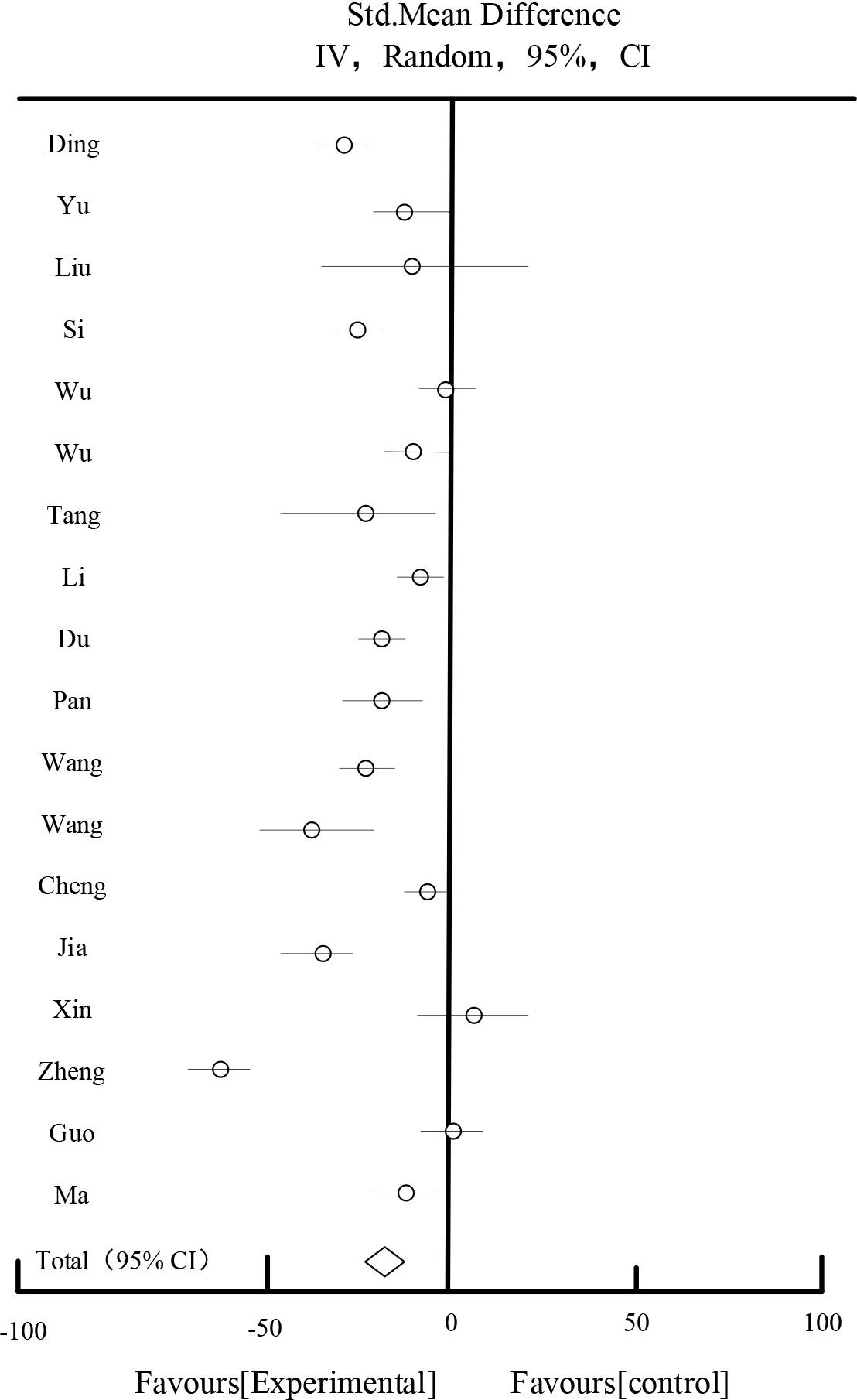
SCR impact results
Table 4 and Figure 4 showed the results of the effect of FBG, 12 studies reported FBG, 709 patients in the test group and 704 patients in the control group, the results of the heterogeneity test showed that: I2=96.23%, suggesting that there was a large heterogeneity between the studies, and according to the P<0.00001, I2=96.23%>50%, so a random-effects model was chosen for the analysis. The results of the Meta-analysis showed that: the rhombus located on the side favoring the experimental group, MD=-0.79, 95%CI [-1.08,-0.39], P<0.0001, the difference was statistically significant, indicating that the experimental group was better than the control group in improving FBG in diabetic nephropathy.
FBG effect
| Study or Subgroup | Experiment | Control | Std,Mean Difference | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Total | Mean | SD | Total | Weight | IV,Random,95%CI | |
| HSN2021 | 6.34 | 0.38 | 128 | 6.48 | 0.32 | 129 | 9.52% | -0.51[-0.64,-0.45] |
| TGQ2018 | 5.82 | 1.26 | 68 | 6.35 | 1.89 | 68 | 7.24% | -0.92[-1.48,-0.32] |
| LT2016 | 7.18 | 0.98 | 35 | 7.12 | 1.02 | 35 | 7.89% | 0.03[-0.48,0.53] |
| WM2017 | 6.25 | 0.62 | 32 | 7.03 | 0.68 | 30 | 8.56% | -0.48[-0.79,-0.12] |
| ZYL2022 | 5.25 | 1.02 | 61 | 6.05 | 1.25 | 60 | 8.25% | -0.67[-1.19,-0.27] |
| DXM2021 | 6.19 | 0.57 | 87 | 6.25 | 0.69 | 87 | 9.05% | -0.15[-0.32,0.08] |
| WZY2021 | 5.32 | 0.63 | 46 | 6.96 | 0.64 | 46 | 8.26% | -1.07[-1.37,-0.79] |
| JF2022 | 6.17 | 0.61 | 45 | 8.15 | 0.92 | 45 | 8.59% | -1.59[-1.87,-1.12] |
| ZJH2017 | 5.32 | 0.82 | 68 | 8.26 | 0.98 | 65 | 8.15% | -2.48[-2.68,-2.14] |
| XSH2014 | 7.19 | 0.73 | 60 | 5.56 | 0.96 | 60 | 8.59% | 0.19[-0.19,0.56] |
| GXY2022 | 5.15 | 0.94 | 38 | 7.26 | 1.03 | 38 | 8.15% | -0.18[-0.59,0.38] |
| MMK2020 | 6.18 | 1.26 | 41 | 7.89 | 1.01 | 41 | 7.75% | -1.38[-1.89,-0.74] |
| Total[95%CI] | 709 | 704 | 100% | -0.79[-1.08,-0.39] | ||||
Heterogeneity:Tau2=0.37,Chi2=231.96,df=10(P<0.00001),I2=96.23%
Test for overall effect Z=4.06(P<0.00001).
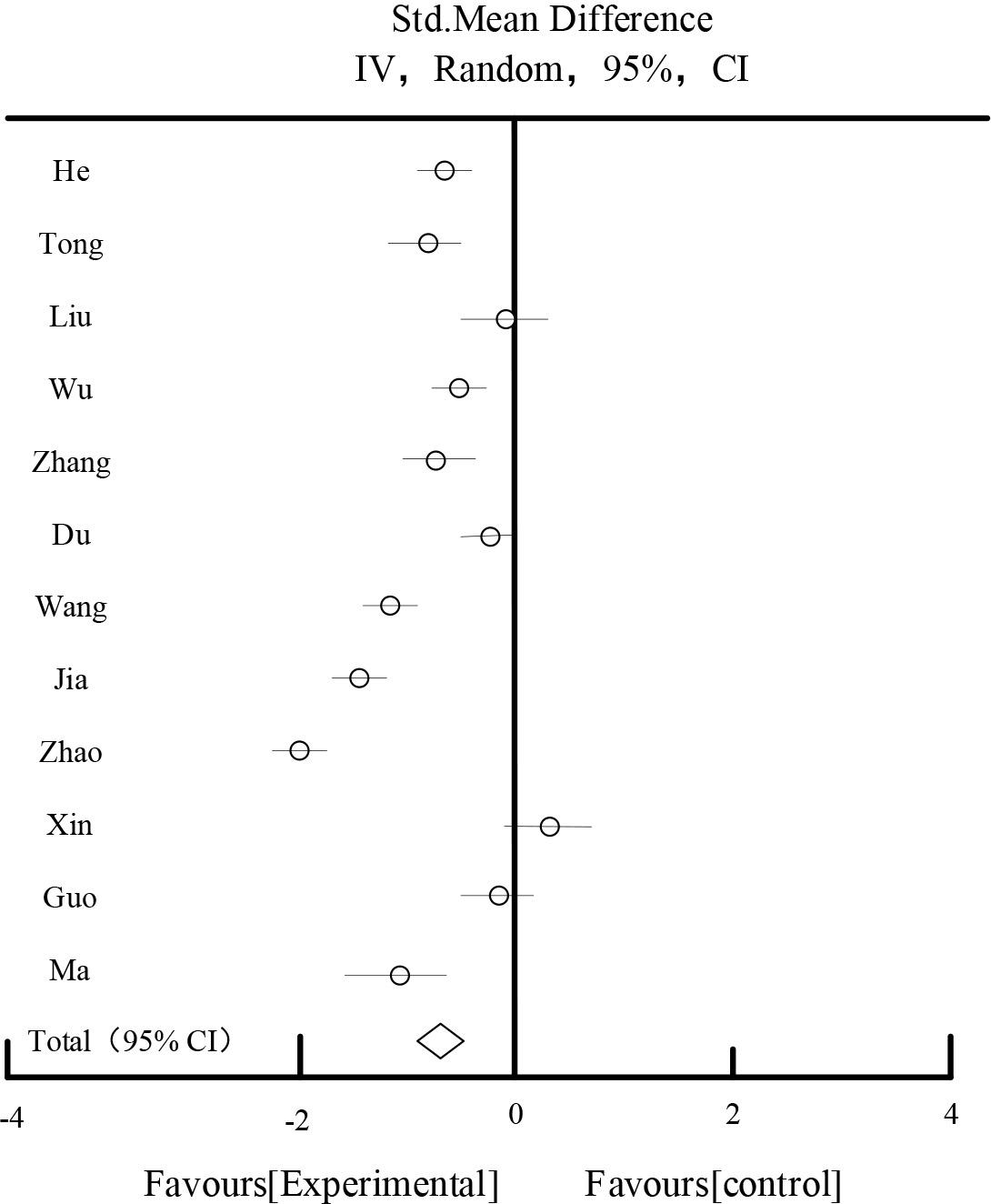
FBG effect
Table 5 and Figure 5 show the results of the effect of 2hPG.A total of 5 studies described 2 hours postprandial glucose, and a total of 754 patients were included. The combined results showed that: there was a large heterogeneity among the studies(I2=82%). After the sensitivity analysis by excluding each study one by one, and different subgroups of analysis targeting the study’s intervention period, drug dosage form, and evidence, the source of heterogeneity still couldn’t be found. A random effect model, MD=-0.58, 95%CI [-0.89,-0.15], P=0.01<0.05, P=0.01<0.15, was used for the study. Random effect model, MD= -0.58, 95%CI [-0.89,-0.15], P=0.01<0.05, the difference was statistically significant, which indicated that the trial group was better than the control group in improving the 2-hour postprandial blood glucose.
The effects of 2hPG
| Study or Subgroup | Experiment | Control | Std,Mean Difference | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Total | Mean | SD | Total | Weight | IV,Random,95%CI | |
| HSN2021 | 9.26 | 0.36 | 128 | 9.29 | 0.36 | 128 | 29.36% | -0.15[-0.21,-0.08] |
| ZYL2022 | 6.23 | 1.83 | 61 | 7.46 | 2.06 | 61 | 14.56% | -1.27[-1.96,-0.56] |
| DXM2021 | 8.56 | 0.89 | 87 | 9.23 | 1.09 | 87 | 24.56% | -0.28[-0.59,0.02] |
| XSH2014 | 8.21 | 1.62 | 60 | 8.49 | 1.49 | 60 | 15.62% | -0.08[-0.79,0.53] |
| MMK2020 | 8.19 | 1.32 | 41 | 9.36 | 1.42 | 41 | 15.90% | -1.17[-1.89,-0.56] |
| Total[95%CI] | 377 | 377 | 100.00% | -0.58[-0.89,-0.15] | ||||
Heterogeneity: Tau2=0.18, Chi2=20.69, df=6(P<0.00001), I2=82%
Test for overall effect Z=2.69(P<0.00001).
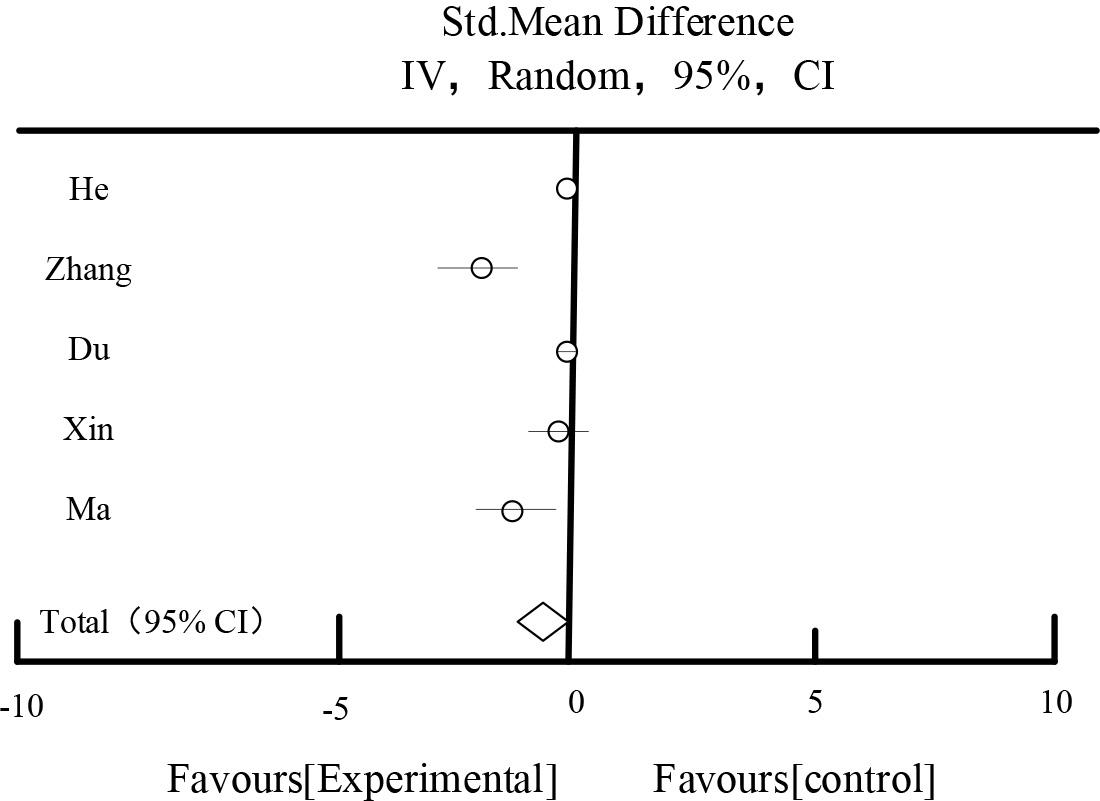
The effects of 2hPG
Table 6 and Figure 6 show the results of the effect of glycated hemoglobin. A total of 9 studies described glycated hemoglobin, a total of 1,070 patients were included,535 patients in each of the control and experimental groups. The combined results showed that: there was a high degree of heterogeneity among the studies(I2=98.56%). After sensitivity analysis by excluding each study one by one and different subgroups of the studies targeting the intervention period, drug dosage form and the diagnostic profile. The random effect model was chosen, the diamond was located on the side favoring the experimental group, MD=-0.69, 95%CI [-1.29, -0.29], Z=3.25, P=0.00005, and the difference was statistically significant, indicating that the experimental group was better than the control group in improving glycated hemoglobin.
Effects of glycosylated hemoglobin
| Study or Subgroup | Experiment | Control | Std,Mean Difference | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Total | Mean | SD | Total | Weight | IV,Random,95%CI | |
| HSN2021 | 6.24 | 0.38 | 128 | 0.38 | 0.35 | 128 | 11.82% | -0.18[-0.26,-0.09] |
| TGQ2018 | 6.32 | 0.78 | 68 | 0.85 | 0.87 | 68 | 11.32% | -0.52[-0.79,-0.26] |
| LT2016 | 6.48 | 0.35 | 35 | 0.56 | 0.52 | 35 | 11.46% | -0.18[-0.34,0.18] |
| WM2017 | 5.56 | 0.32 | 32 | 0.41 | 0.42 | 32 | 11.68% | -1.59[-1.67,-1.36] |
| ZYL2022 | 5.78 | 0.96 | 61 | 1.06 | 1.03 | 61 | 10.58% | -0.95[-1.25,-0.62] |
| DXM2021 | 5.79 | 0.64 | 87 | 0.78 | 0.79 | 87 | 11.69% | -0.78[-0.95,-0.52] |
| JF2022 | 6.56 | 0.45 | 45 | 0.63 | 0.64 | 45 | 11.56% | -1.27[-1.56,-1.03] |
| GXY2022 | 7.15 | 1.29 | 38 | 1.32 | 1.33 | 38 | 9.26% | 0.08[-0.56,0.67] |
| MMK2020 | 6.26 | 0.84 | 41 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 41 | 10.63% | -0.84[-1.14,-0.49] |
| Total[95%CI] | 535 | 535 | 100.00% | -0.69[-1.29,-0.29] | ||||
Heterogeneity: Tau2=0.32, Chi2=256.36, df=7(P<0.00001), I2=98.56%
Test for overall effect Z=3.25(P=0.00005).
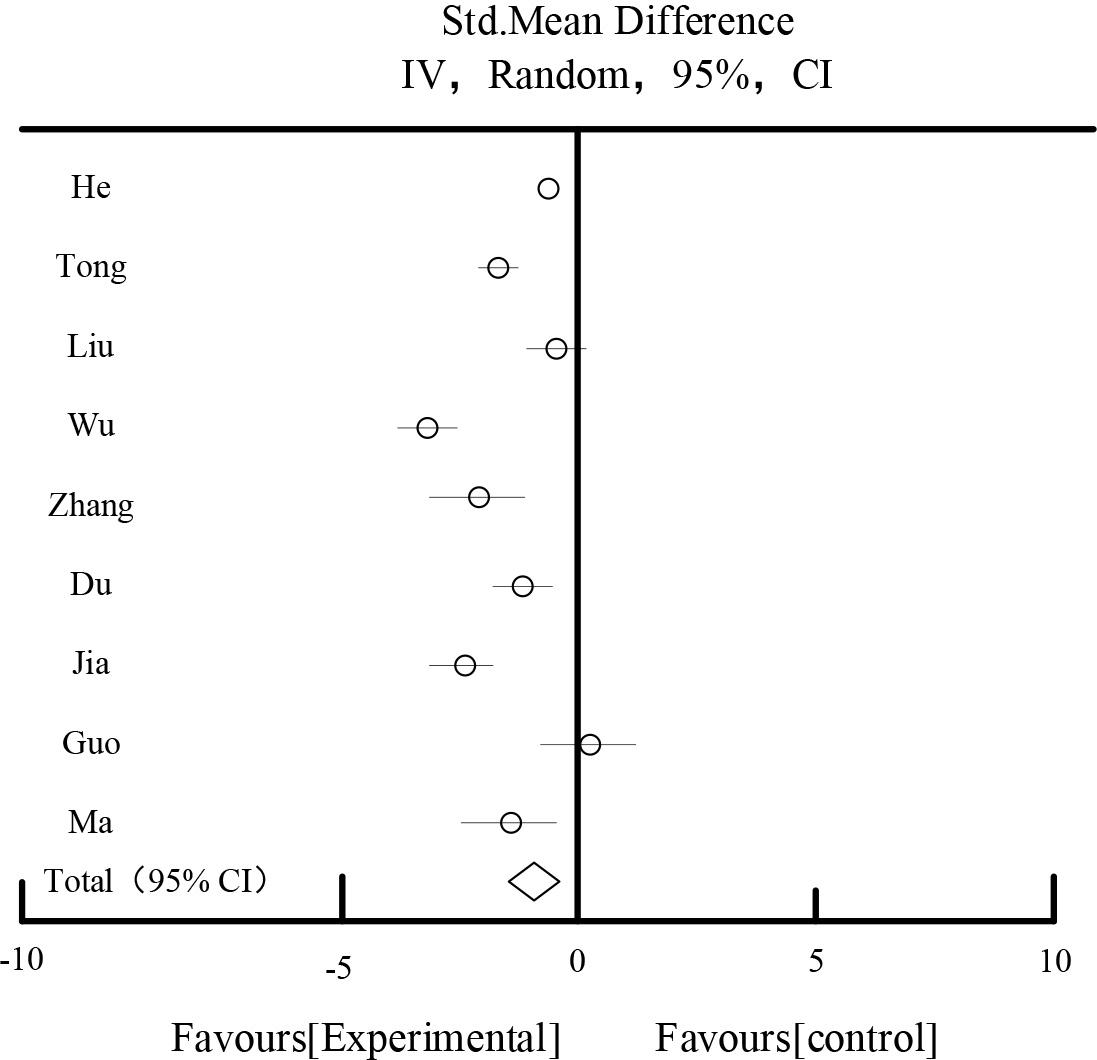
Effects of glycosylated hemoglobin
Table 7 and Figure 7 shows the results of cholesterol effects. Among the included RCTs, a total of 7 studies described cholesterol, and a total of 534 patients were included. The combined results showed: P<0.00001 for heterogeneity test, I2=49%, moderate heterogeneity among studies. Fixed effect model was chosen. Meta-analysis showed that: the test group was more effective in lowering cholesterol than the control group, with an MD: -0.58, 95%CI [-0.67, -0.34].
Cholesterol effect
| Study or Subgroup | Experiment | Control | Std,Mean Difference | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Total | Mean | SD | Total | Weight | IV,Random,95%CI | |
| YFY2011 | 4.56 | 0.78 | 38 | 5.09 | 0.96 | 26 | 9.26% | -0.49[-0.89,-0.05] |
| WS2014 | 5.23 | 1.26 | 34 | 5.95 | 1.15 | 34 | 6.15% | -0.89[-1.25,-0.29] |
| WQG2013 | 5.21 | 1.24 | 59 | 5.53 | 1.36 | 50 | 4.56% | -0.35[-0.97,0.32] |
| CJH2017 | 5.18 | 1.29 | 40 | 5.24 | 1.32 | 42 | 5.29% | -0.09[-0.67,0.6] |
| LWM2016 | 4.26 | 0.42 | 32 | 4.97 | 0.45 | 30 | 32.25% | -0.67[-0.98,-0.45] |
| CXB2013 | 3.25 | 0.86 | 31 | 4.26 | 0.62 | 30 | 11.26% | -0.93[-1.24,-0.59] |
| HSH2018 | 4.19 | 0.47 | 43 | 4.49 | 0.48 | 45 | 31.23% | -0.38[-0.57,-0.12] |
| Total[95%CI] | 277 | 257 | 100.00% | -0.58[-0.67,-0.34] | ||||
Heterogeneity: Tau2=0.58, Chi2=11.26, df=9(P<0.00001), I2=49%
Test for overall effect Z=7.69(P<0.00001).
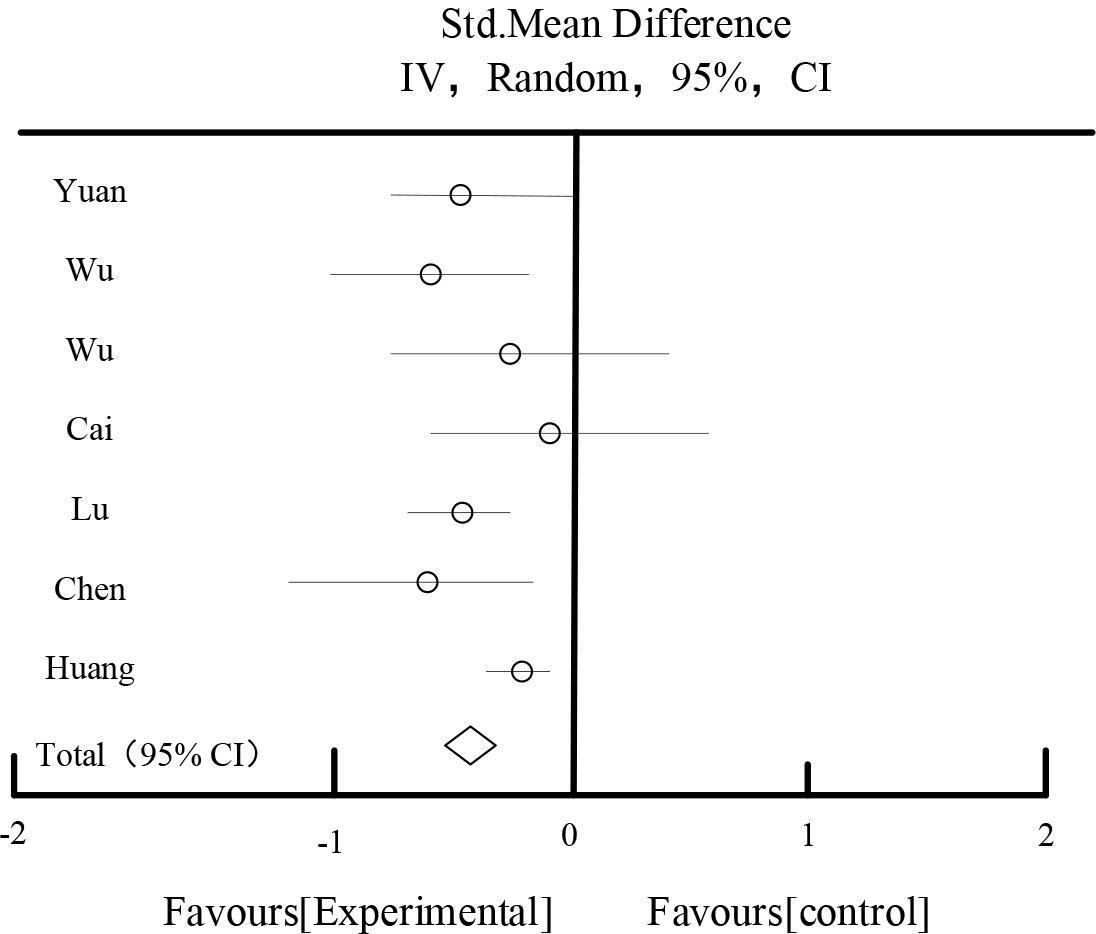
Cholesterol effect
Table 8 and Figure 8 show the results of the effect of triglycerides. Among the included RCTs, a total of 7 studies described triglycerides and a total of 534 patients were enrolled. The combined results showed: Heterogeneity test P=0.29, I2=23%, moderate heterogeneity among studies. Fixed effect model was chosen. Meta-analysis showed that: the test group had a better effect on lowering triglycerides than the control group. MD: -0.37, 95%CI: [-0.48, -0.29].
Effects of triglycerides
| Study or Subgroup | Experiment | Control | Std,Mean Difference | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Total | Mean | SD | Total | Weight | IV,Random,95%CI | |
| YFY2011 | 0.81 | 0.18 | 38 | 1.18 | 0.29 | 26 | 45.00% | -0.38[-0.49,-0.23] |
| WS2014 | 2.03 | 0.56 | 34 | 2.56 | 0.56 | 34 | 9.56% | -0.57[-0.78,-0.28] |
| WQG2013 | 1.79 | 0.84 | 59 | 1.79 | 1.24 | 50 | 2.23% | -0.03[-0.57,0.58] |
| CJH2017 | 1.53 | 0.83 | 40 | 1.64 | 0.83 | 42 | 4.21% | -0.12[-0.49,0.27] |
| LWM2016 | 1.89 | 0.67 | 32 | 2.23 | 0.59 | 30 | 5.59% | -0.37[-0.67,-0.08] |
| CXB2013 | 1.75 | 0.63 | 31 | 2.34 | 0.98 | 30 | 3.25% | -0.68[-1.06,-0.29] |
| HSH2018 | 1.59 | 0.34 | 43 | 1.85 | 0.31 | 45 | 30.16% | -0.27[-0.42,-0.19] |
| Total[95%CI] | 277 | 257 | 100.00% | -0.37[-0.48,-0.29] | ||||
Heterogeneity: Tau2=1.29, Chi2=7.78, df=4(P=0.29), I2=23%
Test for overall effect Z=8.59P<0.00001).
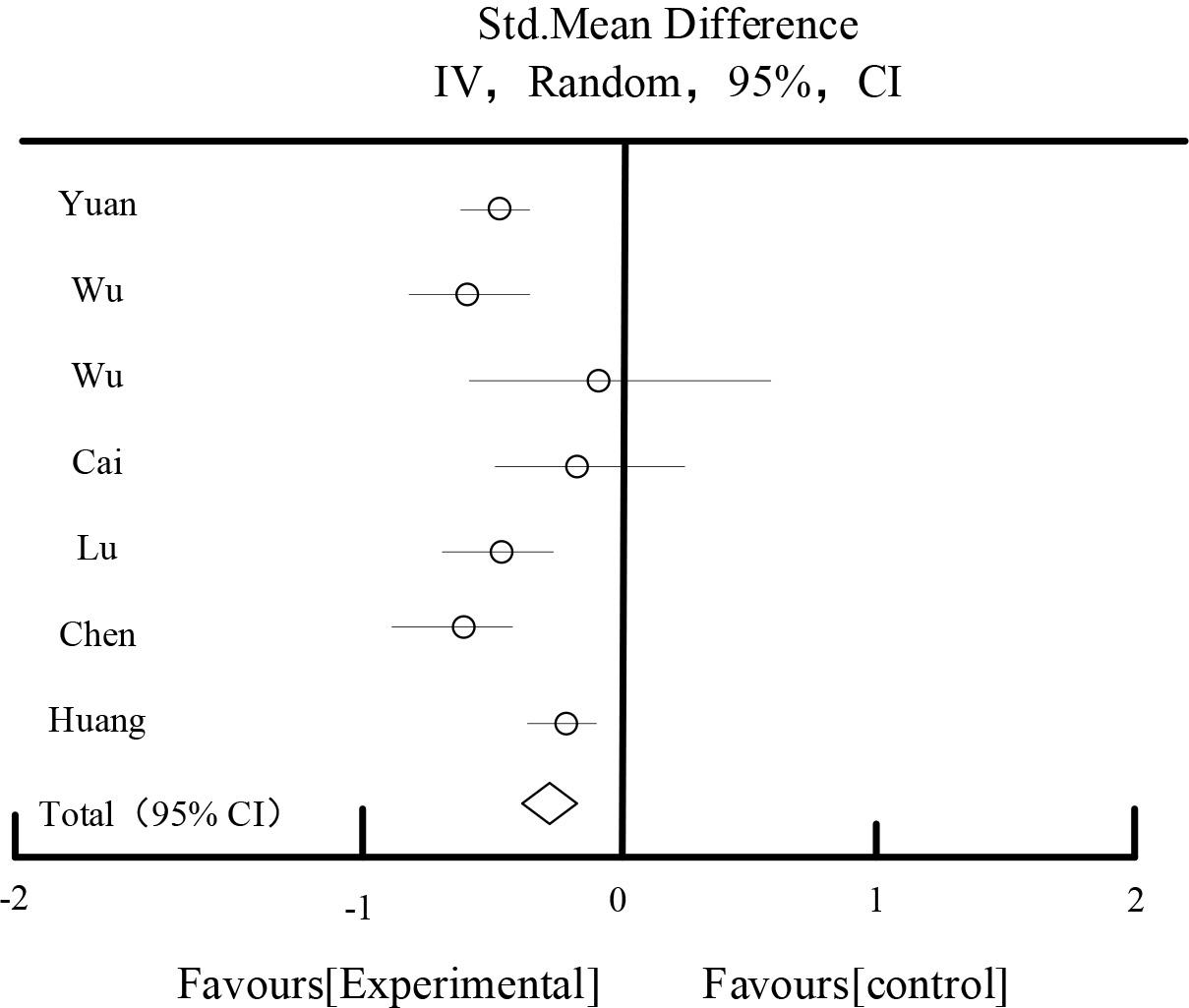
Effects of triglycerides
Table 9 and Figure 9 show the adverse reactions, out of the included literature, 11 of these studies reported the number of cases of adverse reactions. The adverse reactions were mainly mild gastrointestinal reactions such as nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, hypoglycemic reactions, mild dizziness and headache, which were relieved to disappear after symptomatic treatment. The counts of adverse reactions of the 11 studies were analyzed for statistical results, and the difference between the two groups was found to be statistically significant [Chi2=13.26, df=19 (P=0.16), I2=29%] [OR=0.79, 95%CI [0.54,1.12], Z=1.56(P=0.19)], which suggests that applying traditional Chinese medicines to improve inflammatory reactions in patients with early-stage DKD Safer.
Bad reflection
| Study or Subgroup | Experiment | Control | Std,Mean Difference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Events | Total | Events | Total | Weight | IV,Random,95%CI | |
| DL2022 | 3 | 59 | 3 | 59 | 4.48% | 1.45[0.24,6.25] |
| YZX2019 | 9 | 38 | 7 | 38 | 7.59% | 1.42[0.41,4.66] |
| LT2016 | 5 | 35 | 7 | 35 | 10.23% | 0.67[0.19,2.45] |
| SYL2015 | 3 | 86 | 4 | 86 | 5.36% | 0.67[0.18,4.18] |
| WBJ2020 | 7 | 46 | 9 | 46 | 10.26% | 0.82[0.29,2.79] |
| WYP2019 | 1 | 42 | 2 | 42 | 1.79% | 1.87[0.19,23.36] |
| TCQ2021 | 1 | 45 | 2 | 45 | 0.89% | 5.24[0.29,113.26] |
| LQ2021 | 3 | 50 | 4 | 50 | 32.96% | 0.048[0.00,0.29] |
| DXM2021 | 5 | 87 | 4 | 87 | 4.68% | 1.43[0.37,6.25] |
| PXQ2016 | 9 | 45 | 10 | 45 | 6.26% | 1.28[0.31,4.56] |
| WL2019 | 11 | 59 | 10 | 59 | 15.50% | 0.97[0.37,2.66] |
| Total[95%CI] | 57 | 592 | 62 | 592 | 100% | 0.79[0.54,1.12] |
Heterogeneity: Tau2=5.36, Chi2=13.26, df=19(P=0.16), I2=29%
Test for overall effect Z=1.56(P=0.19).
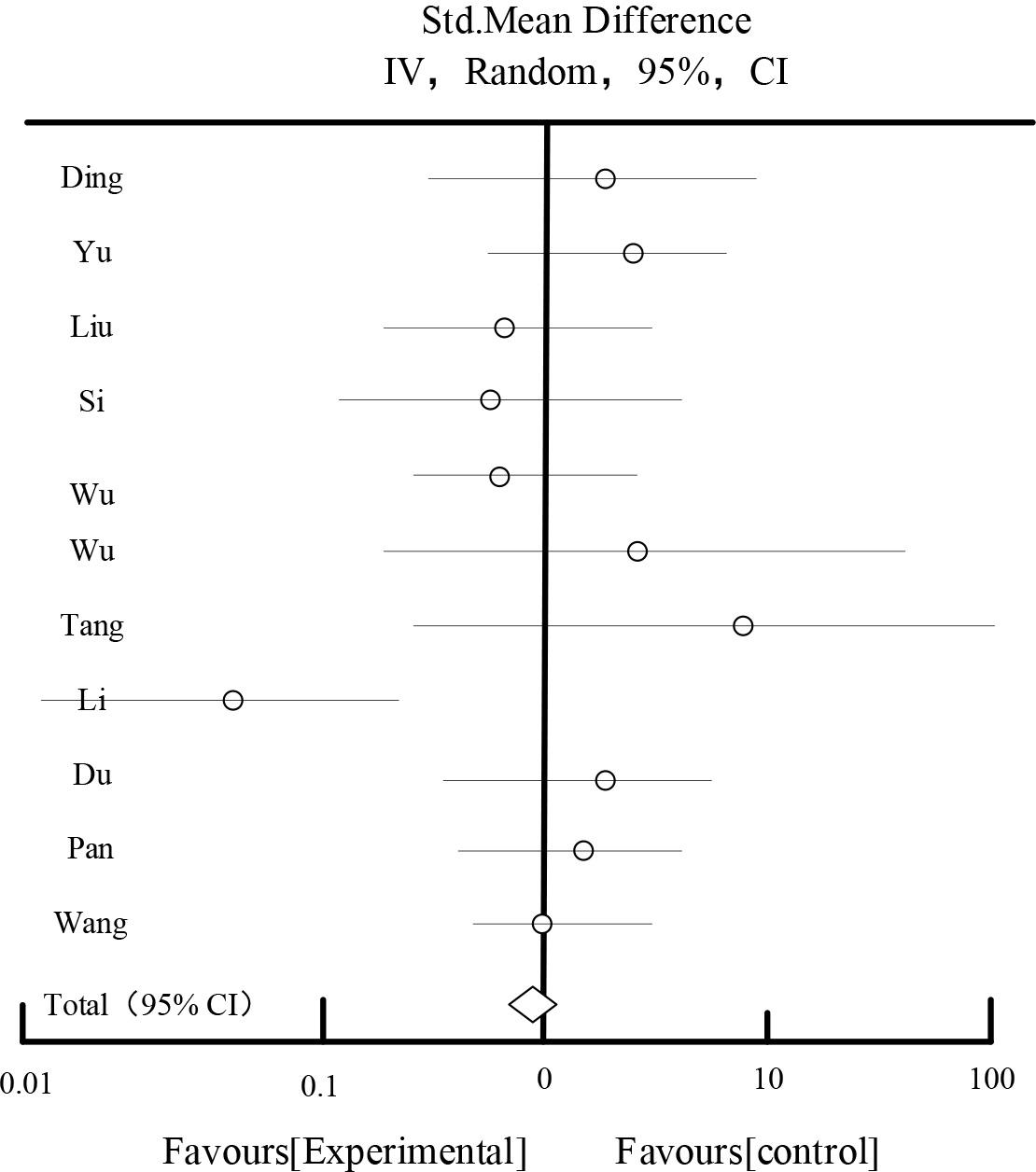
Bad reflection
Figure 10 shows the graph of risk of bias assessment for inclusion in RCTs. In terms of generation of randomized sequences, a total of 79 trials out of 100 studies reported the method of generating randomized sequences, using randomized number tables or computerized randomized allocation, and 21 studies described only “random” without reporting the specific method, which made it impossible to determine the risk of bias. In terms of concealment of randomization, the trials described a method of concealment of randomization in which the study center or drug administrator controlled the allocation scheme and numbering was done in closed, opaque envelopes so that clinicians and subjects could not predict the allocation sequence. 25 studies were unable to determine the risk of bias. In terms of implementation of blinding, 27 studies described placebo consistently given to the control group, which was associated with a low risk of bias, and the remaining 68 studies did not use placebo, which was associated with a low risk of bias. In the blinding method, 27 studies described a consistent placebo for the control group, with a low risk of bias, while the remaining 68 studies did not use a placebo, with a high risk of bias.

Inclusion of RCT bias risk assessment
In terms of blinded evaluation of outcomes, only 13 studies reported statistical analysis of data information by a third-party independent organization, 18 studies were unclear whether the data information was blinded or not, and another 70 studies had a high risk of measurement bias.
In terms of follow-up bias, there was between-group balance for all included RCTs with complete or missing data on outcome indicators, and 95 studies described criteria and methods for exclusion or dislodgement with low follow-up bias.
In terms of reporting bias, most studies did not have sufficient information to judge the level of risk of bias.
In terms of other sources of bias, most studies also did not have sufficient information to evaluate whether there was a significant risk of bias. In conclusion, the methodological quality of the 100 RCTs was partially low.
Based on the etiology and pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy, this paper proposes the treatment of Chinese medicine from four aspects, including dialectic typing. Meta-analysis was utilized to systematically evaluate the treatment of diabetic nephropathy with TCM. The therapeutic effects of TCM on diabetic nephropathy were evaluated by controlled experiments, respectively, from eight outcome indicators. Meanwhile, adverse effects and bias were evaluated to assess the risks associated with TCM treatment.In Meta-analysis, the results of heterogeneity test of UAER outcome indexes I2=94.36%, SMD=-1.92, 95%CI [-2.59, -1.33], P<0.00001, the difference was statistically significant, which indicated that the herbal treatment was better than the control group in improving the UAER in diabetic nephropathy. The adverse effects of the Chinese medicine trials were analyzed, and the difference between the two groups was statistically significant when 11 studies reported adverse effects in the literature, [Chi2=13.26, df=19 (P=0.16), I2=29%] [OR=0.79, 95% CI [0.54,1.12], Z=1.56 (P=0.19)], which indicated that the application of Chinese medicines to improve the inflammatory response in patients with early DKD is safer.Plotting the risk of bias assessment of the included RCTs, in terms of follow-up bias, 95 studies had a low follow-up bias. Overall, the methodological quality of the 100 RCTs tested was partially low.
