Exploration of the Development Path of Enterprise Accounting Informatisation - Based on the Perspective of Industry-Finance Integration
Data publikacji: 17 mar 2025
Otrzymano: 02 lis 2024
Przyjęty: 07 lut 2025
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/amns-2025-0191
Słowa kluczowe
© 2025 Ziping Li, published by Sciendo
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
In recent years, China’s digital economy has developed one after another, and all kinds of digital technologies have been widely used in different fields, laying a solid foundation for people’s lives and social development. From this aspect, it can be seen that in the era of the digital economy, the rapid development of science and technology has led to the rapid rise of the digital economy, which has injected a brand new vitality into social and economic development and has become a new driving force to pull China’s economic growth [1-4]. In social development, enterprises that want to improve their social value and economic benefits must effectively do a good job of information technology construction work, especially enterprise accounting information technology construction. At present, Chinese enterprises in the construction of accounting informatisation mainly rely on computer technology, which significantly improves the efficiency of work and is an important guarantee to promote the long-term development of enterprises [5-8].
Accounting informatisation is a new way for enterprises to use accounting systems to analyse and process financial data, which is a product of the development of the information age, and the improvement and development of accounting informatisation systems is an inevitable requirement for the long-term operation of enterprises [9-11]. The application of informatisation can promote the efficient recording of payments and the closing of accounts at the end of the period, help accountants to process different accounting information, provide basic protection for the long-term development of enterprises, and further promote the progress and development of enterprises. At this stage, the development of enterprise accounting information technology is of great significance to the integration of business and finance, which is also known as “business and finance integration”, and plays an increasingly important role in the production and operation activities of enterprises [12-15].
Literature [16] discusses the impact of accounting information technology on enterprise financial management in the era of big data. The experimental class and control model was established and analysed to point out that the benefit and informatisation improved the efficiency of accounting positions, but information technology also brought many security risks. Literature [17] examines the importance of enterprise accounting informatisation and the problems faced in its management, and introduces effective measures for enterprise accounting informatisation management in the context of big data. Literature [18], based on the problems exposed in the construction of enterprise accounting informatisation in the context of the big data era, puts forward suggestions such as improving the protection of accounting information systems and formulating security regulations, aiming to promote the development of accounting informatisation. Literature [19] starts from the connotation of accounting informatisation, develops an analysis of the current situation of accounting informatisation in China and the challenges that exist, which include the low quality of accounting practitioners and the lack of comprehensive talents, etc., and suggests strategies to address these challenges. Literature [20] reveals that the business level of financial personnel in most Chinese enterprises varies, and improving their business competence level requires enterprises to pay attention to financial knowledge and the application of management accounting and its information system in the training process. Literature [21] discusses the impact of accounting informatisation on the financial management of enterprises on the premise of analysing the existing information and proposes corresponding initiatives. It is emphasised that accounting informatisation enables the automatic processing of data and ensures the accuracy and timeliness of financial data. Literature [22] aims to reasonably avoid and reduce the risks in the accounting information system and discusses the corresponding solutions for its risks to ensure the truthfulness and reliability of enterprise information data.
In this paper, the enterprise accounting information management system is constructed with the background of industry-finance integration and based on the enterprise goals of scientific operation, effective resource allocation, risk control, performance management and so on. It also collects internal information and public information of the company in the way of interviews, and combs and analyses the data related to the mined implementation of the accounting information management system through OLAP multidimensional analysis technology. The system of this paper is applied to Company A, and a questionnaire survey is used to rate the accounting informatisation management system under the perspective of industry-financial integration, and finally, the hierarchical analysis method is used to further analyse the effect brought by the system of this paper in the development of accounting informatisation.
Enterprises in the context of the integration of business and finance information technology construction, in order to grasp the functions, positioning and value of business finance and finance on the basis of organisational change, reconstruct the performance evaluation system, the financial integration of business, can achieve scientific business analysis, effective resource allocation, comprehensive risk management and quantitative performance management objectives, and comprehensively help to enhance the value of the enterprise.
Scientific business analysis
The integration of business finance needs to scientifically and effectively analyze the business situation and effectively grasp the business bottlenecks. With the construction of enterprise accounting information technology, enterprises can incorporate budget indicators and requirements into the system for daily control through the financial system, help enterprises achieve the targets and provide feedback verification, and collect timely information through the business terminal to ensure that there is no deviation from the business objectives.
Effective resource allocation
Enterprises can build a perfect budget management system through the construction of accounting information technology to allocate resources more effectively. Through the scientific and comprehensive information technology accounting management system, enterprises can take advantage of the overall operation of the financial sector, the enterprise resources for a more scientific and reasonable distribution, to avoid waste of resources. For enterprises to promote the integration of industry and finance, financial managers can base on the enterprise’s actual production and sales activities for financial management to avoid the situation of mindlessly investing resources and enhance the comprehensiveness and directionality of enterprise resource allocation.
Comprehensive risk management and control
Enterprise accounting information technology construction facilitates the gradual integration of enterprise financial management, business operations, and transformation, and plays a common role. Enterprises after an in-depth study of their industry financial integration of financial systems and features, so that it can be more comprehensive according to the enterprise in the industry financial integration of the development process of the risk characteristics of the construction of the enterprise’s information for a more accurate refinement, and strive to fundamentally analyse the scale of the investment, management plans, and the return of capital to provide a basis for the use of the capital can be used to monitor the status of the immediate and effective reduction of the financial risk of the enterprise. Risks.
Quantitative performance management
Enterprises will directly decompose the main responsibility of performance appraisal management down to the specific financial budget management department to ensure that the enterprise’s capital investment is reasonable, efficient, and safe to use and improve the efficiency of capital management. In addition, the quantitative assessment standards for enterprise performance management can be directly linked to actual performance and provide performance feedback, prompting departments to independently improve work efficiency. By analysing the business drivers of financial information, it helps to define the business departments responsible for the fluctuation of financial information, forming a virtuous circle within the enterprise and making the information of each department of the enterprise more open and transparent, which can effectively improve the work efficiency of the personnel of the enterprise.
The basic process of data mining is shown in Figure 1. It is divided into three stages: data preprocessing, data mining, and result analysis [23-24].
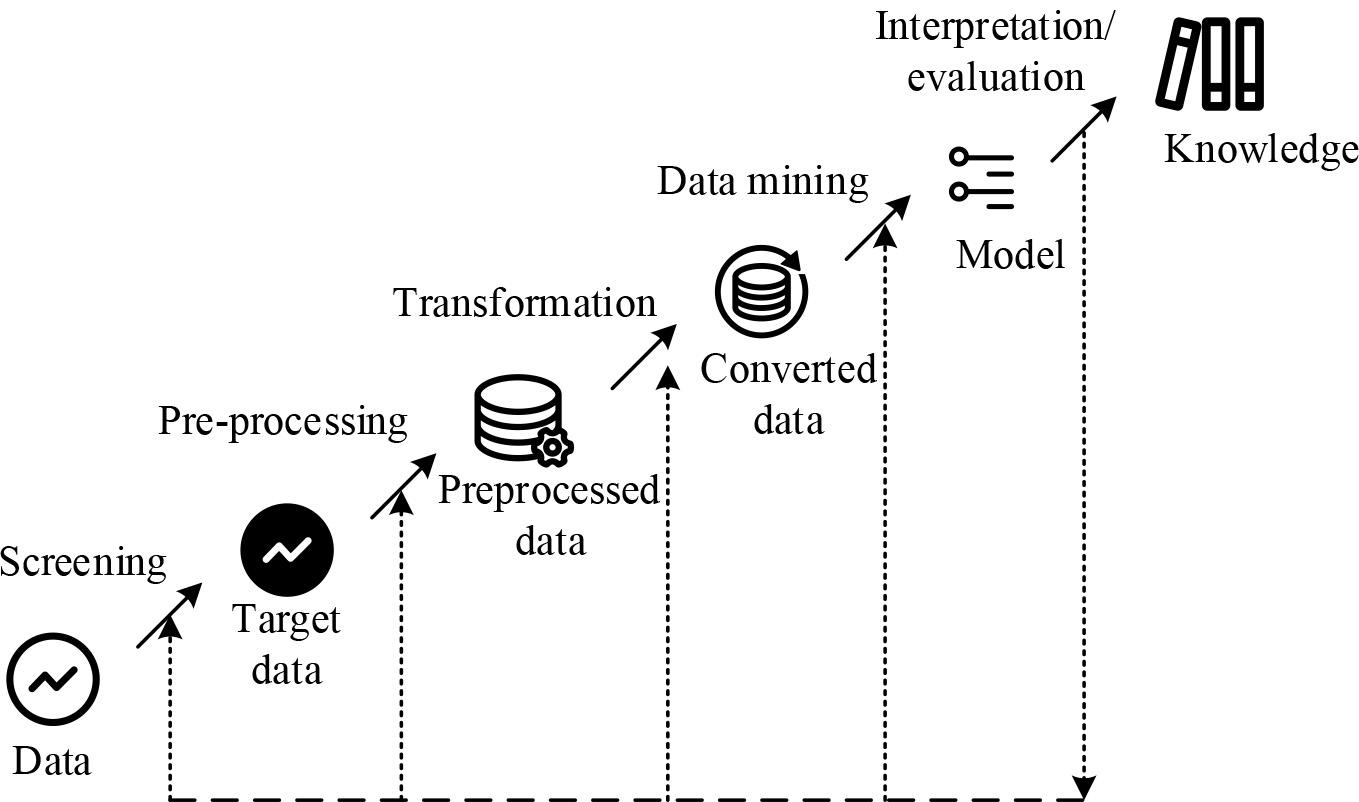
General process of data mining
The methods of data preprocessing are:
Data cleaning: eliminating noise in data processing to correct inconsistencies. Data Integration: Integrate various data sources into a unified information database to form an overall data set, i.e., a data warehouse. Data Transformation: Using techniques of aggregation, redundancy removal, or clustering to compress data. Data Statute: Transform data in one format into another format, such as normalisation.
The pre-processed data has the characteristics of accuracy, completeness, consistency and interpretability.
OLAP is to first organise the data in the database in a multidimensional way and then combine the slicing, dicing, rotating and drilling operations to complete the combing and analysis of different dimensions and different types of massive and complex data [25-26].
Slicing and chunking
The study of selecting a particular dimension in a given multidimensional data structure is called slicing, and the resulting two-dimensional planar data is obtained through this operation. The slicing operation is the superposition of multiple slicing operations, and what is obtained is a subcube, i.e., a study that selects two or more dimensions in a multidimensional data structure.
Rotation
The position of the dimensions in the table is partitioned, and the change in the order in which the dimensions are arranged allows one to observe and analyze the data from different viewpoints. Common methods include changing rows and columns, converting the dimensions of a column to a row, or converting the dimensions of a row to a column.
Drill-down
Drill-down is to convert the level of dimensions, transforming the analysis of granularity, and can be divided into two types of operations: volume and drill-down.Upscrolling is the process of realizing fine-grained data aggregation at a higher level and overlaying data in the data cube by increasing the dimensional level, which facilitates the overview statistics of the data.Drill-down is the inverse of up-scrolling, where the aggregated data is refined into finer-grained data along the dimensional hierarchy.
This paper uses hierarchical analysis to process the data recovered from the questionnaire.
The judgement matrix A is constructed according to the scoring results of the hierarchical analysis method.
Use the sum and product method to normalise the data of judgment matrix A column by column.
Organize the results of column-by-column normalization into a normalized judgement matrix
The normalised judgement matrix is summed row by row to compute the eigenvector
The feature vector
The set of feature vectors
Consistency test of judgement matrix
Fill in the judgement matrix to construct the subjective evaluation matrix. In order to further ensure its scientific and effectiveness, it is also necessary to use the consistency test to determine whether there is a logical error in the constructed judgement matrix. If it does not pass, then the judgement matrix needs to be reconstructed.
Calculate the maximum characteristic root
Where (
Calculate this judgement matrix consistency metric:
Calculate the consistency ratio:
As the dimension of the judgment matrix increases, the degree of consistency of the judgment decreases, so the consistency requirement should be relaxed for high-dimensional judgment matrices. In order to make corrections, the stochastic consistency indicator RI is introduced. The uniform values of RI are shown in Table 1. Note: The source of the data in the table is the AHP average stochastic consistency indicator RI values taken.
| N | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| RI | 0 | 0 | 0.58 | 0.90 | 1.12 | 1.24 | 1.32 | 1.41 | 1.45 |
The consistency ratio is a more reasonable measure of judgement matrix consistency and is calculated as:
When the consistency ratio is
Questionnaire recovery
Through the retrieval of questionnaires on the evaluation of the effect of industry and financial integration of five dimensions and the importance of specific indicators under the dimensions compared with each other, the construction of the judgement matrix, the use of hierarchical analysis to calculate the weights of the indicators. The importance rating template for the five evaluation dimensions and specific indicators within each dimension is shown in Table 2.
| Index | Financial performance | Market performance | Decision management | Innovative learning | Business integration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Financial performance | |||||
| Market performance | |||||
| Decision management | |||||
| Innovative learning | |||||
| Business integration |
In this paper, an accounting information management system is constructed by combining the technical characteristics of the information system with business and finance integration.The overall structure of the accounting information management system is shown in Figure 2.
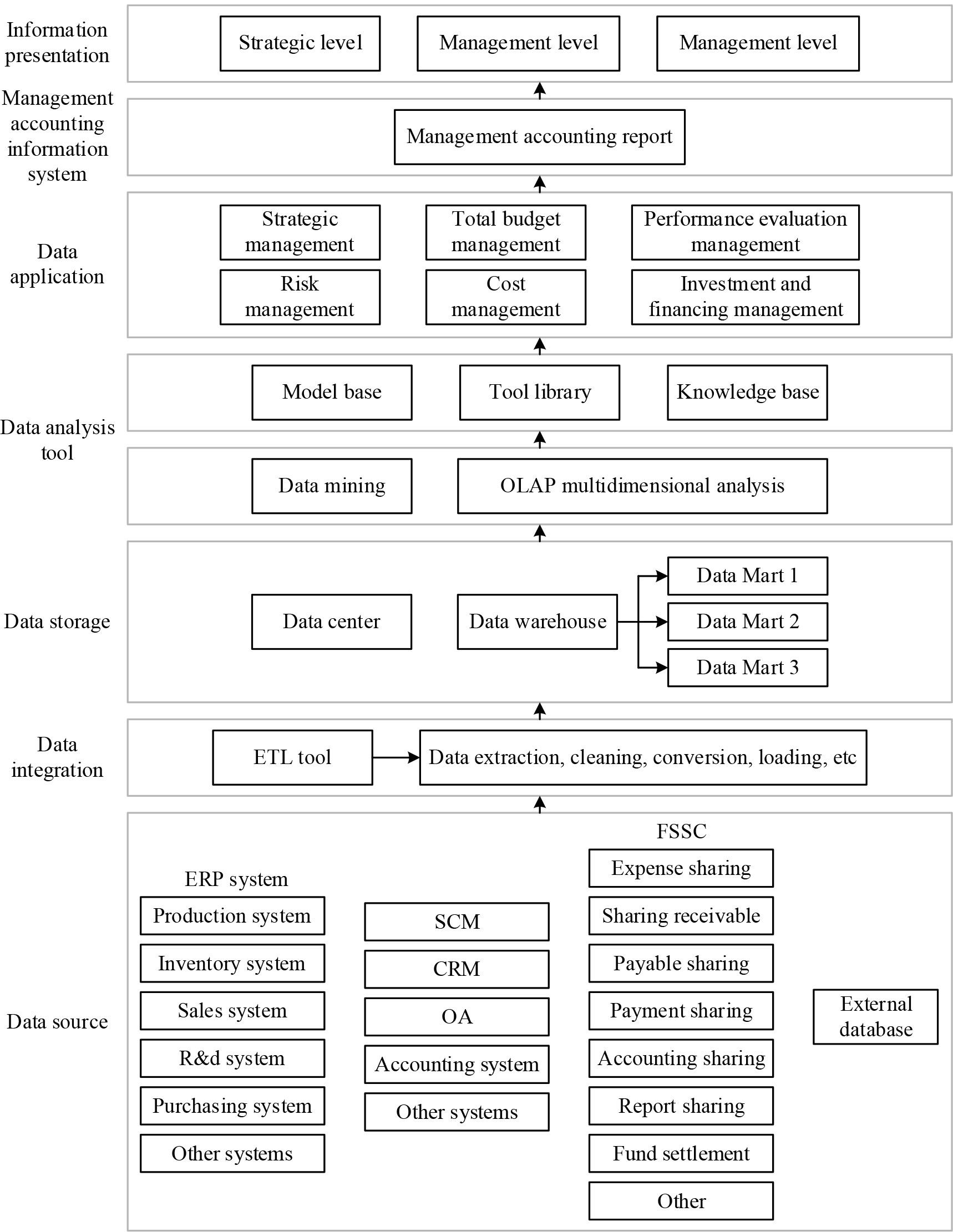
The overall architecture of the information accounting management system
In the era of big data, the effective development of enterprise management should not only focus on internal “small data” but also pay attention to external “big data”. The information-based accounting management system is based on a large amount of internal business, financial information and external data, and through the built-in data processing algorithms, it collates, analyses and processes them to form useful information. The main data sources of the system mainly include internal data sources and external data sources, which are dispersed in various systems of the enterprise and external information systems, so the system in this paper adopts an open data connection method to achieve automatic data collection from other related systems. In addition, this paper conducts data mining on relevant information before and after Company A uses the system in the following ways.
Interviews
The financial managers and business managers of Company A were interviewed separately, and each interview lasted about 1-2.5 hours.The primary objective of this study is to determine how to implement the accounting information management system and how to apply it. Based on the interviews with the managers, informal interviews with other business personnel were also conducted to obtain relevant information about the implementation of management accounting information systems from the perspective of business personnel.
Internal company information
Internal newspapers and journals of Company A were obtained by mail and email, as well as the staff operation manual for the implementation of the management accounting system, the contents of the classroom materials for staff-related training, and the minutes of the relevant regular meetings of the company were also obtained. In addition, we also obtained information related to the company’s publicity activities on campus, accumulating a large amount of information for the study.
Public Information
The relevant information was obtained by checking the official website of Company A. By the fact that Company A is a listed company, the relevant public information is very rich, and by browsing the relevant information released by the Shenzhen Stock Exchange, the information on the enterprise’s annual report for 2018-2023 was obtained, as well as the news reports related to the enterprise.
The accounting information management system first uses Extract-Transform-Load (ETL) tools to select useful data and extract it from relevant systems and then unifies the heterogeneous data collected from different source systems into a unified format after cleansing, transforming, and reconstructing operations. These data are then effectively integrated and loaded into a data warehouse (DW) for storage, forming an enterprise-level big data center.
DW front-end data mining (DM) tools and online analytical processing (OLAP) tools, the system can use DM tools for data in the data centre to conduct in-depth mining, extract the hidden data with potential value, and in-depth discovery of different data logic, correlation and mapping between the relationship between the data and the business activity entity, and can establish the corresponding data model. And combined with OLAP to carry out rapid, flexible, multi-dimensional, multi-level data analysis.
Accounting information management system is divided into different functional modules according to different contents, and the information output of each module and the result of information operation can be shown to different information demand users of the enterprise in various ways, such as visual interface, word document and pdf file. The use of information technology to achieve the automatic generation of management accounting reports and real-time export, but also the use of BI provides a powerful visualisation technology with a variety of easy-to-understand graphical forms to the various business activities in real-time, intuitive, multi-dimensional display.
The business-finance integration accounting information management system refers to the accounting information system that can realise business-finance integration, which is an effective platform and tool for enterprises to realise business-finance integration by using various modern computer technologies. The enterprise’s financial work is done in advance for the business side.Through the system, enterprises can not only obtain financial analysis of management information, but also directly obtain information related to management from business data.Managers can use the business side of the information for more in-depth analysis to achieve the integration of information and data flow.
The functions of the accounting information management system based on the integration of industry and finance are shown in Figure 3. The accounting information management system based on the integration of business and finance realises the information sharing of business and financial data, breaks through the limitations of traditional accounting system management, and improves the utilisation rate of business information. It promotes the integration of accounting and management in a more comprehensive manner, making accounting a significant aid to enterprise management.The results of decision-making and management by managers through business information and financial information can, in turn, be reflected in business activities and promote the improvement of the quality of business activities.
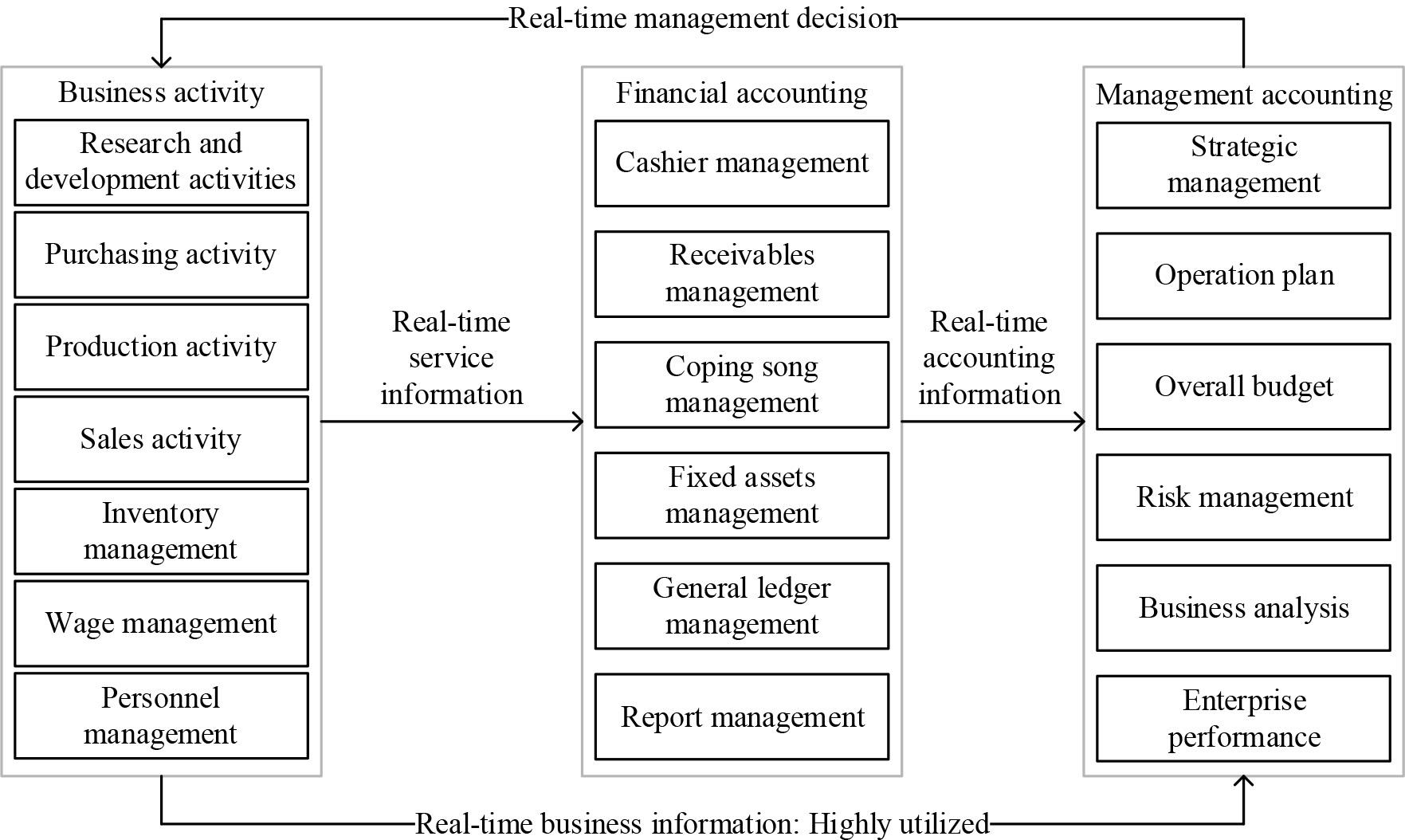
AIS function diagram for integrating industry and finance
For the accounting informatisation management system designed in this paper, the level of informatisation construction of the system in Company A’s business-finance integration effect is analysed from four operational indicators, namely, inventory turnover, accounts receivable turnover, current asset turnover, and total asset turnover, to further evaluate whether the system can provide more accurate information for the decision makers of the company. Figure 4 shows the trend of the 4 operational indicators in Company A over the last six years.
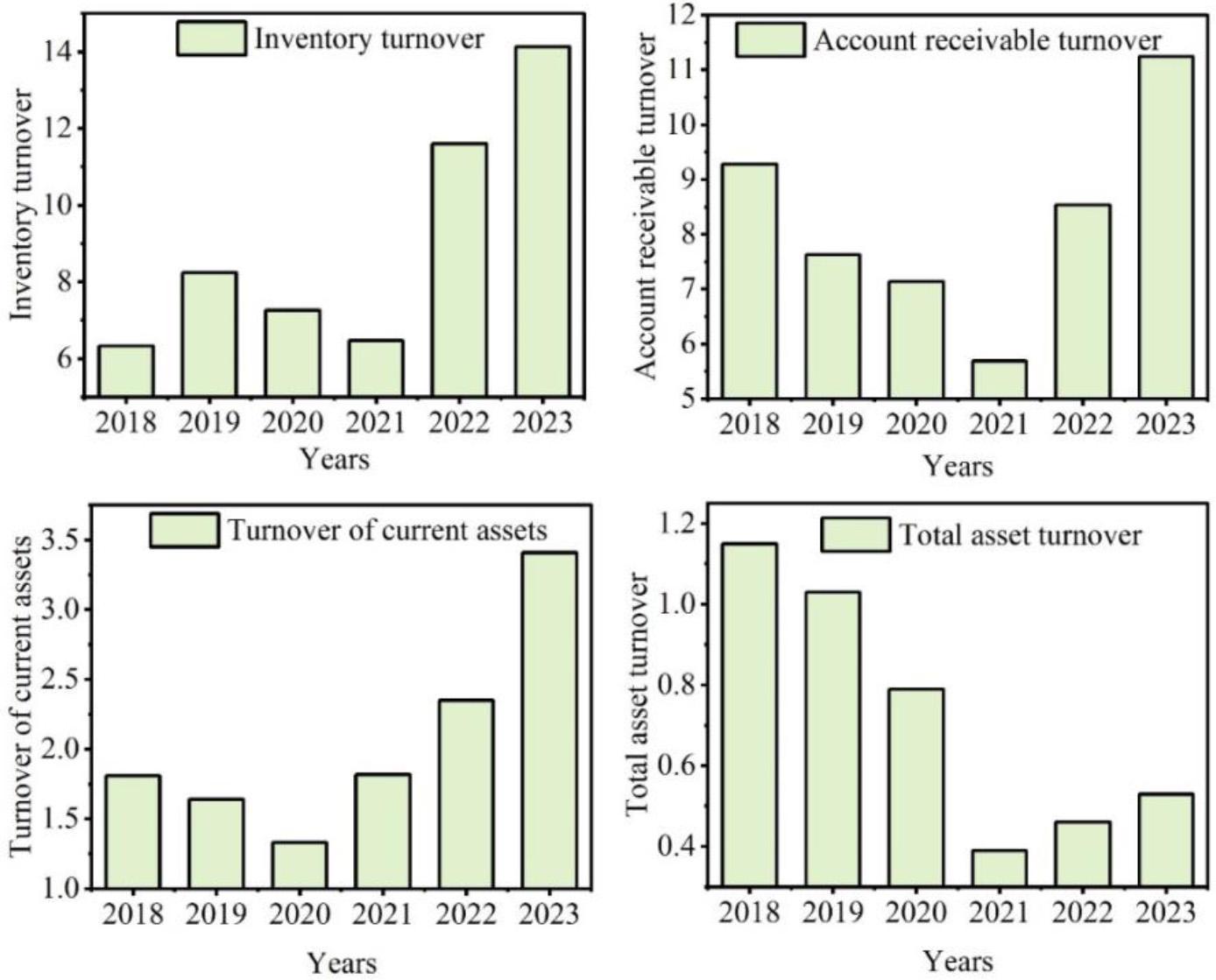
The change of 4 operating indicators in the company in nearly six years
After the implementation of the system in this paper in 2022, the following conclusions will be drawn based on the analysis of each operational indicator:
Company A’s inventory turnover and accounts receivable turnover showed a turnaround in 2021, and it is not difficult to find a gradual increase in the trend after 2021. In the years before 2021, the accounts receivable turnover ratio and inventory turnover ratio decreased respectively until 2021, reaching 6.47 and 5.69 respectively. However, after this year, the upward trend of the inventory turnover ratio and accounts receivable turnover ratio was very obvious, and in 2023, they had increased to 14.13 and 11.25, respectively. The investigation and research found that, in 2021, in conjunction with the integration of the business and financial accounting information technology management system, Company A started to prepare for business reorganisation. Therefore, we can infer that the information technology construction based on the integration of business and finance has helped Company A improve its inventory management and accounts receivable management, and accelerate the inventory flow and capital turnover.
The current asset turnover ratio of Company A shows a decreasing trend before 2020, which indicates that the enterprise’s liquidity use is inefficient and profitability still needs to be further improved. The current asset turnover ratio rises after 2020, among which the rising trend is more significant in 2022-2023, with an increase of 1.06, which is mainly related to the fact that the application of the system in this paper makes the asset reorganisation lead to a significant increase in operating income.
Total asset turnover is an important indicator of the quality of all asset management services, operating capacity and other comprehensive assessments of the enterprise, generally regarded as the absolute amount of the average sales revenue and the average net operating assets during the operating period of the enterprise, the faster the turnover rate, indicating that the enterprise’s overall operating management services, the weaker the ability. As can be seen from the figure, the total asset turnover ratio of company A showed a downward trend from 2018 until 2021, when it dropped to 0.39, and the enterprise’s asset utilisation efficiency was low. 2022, with the application of the accounting information management system of industry and finance integration, the total asset turnover ratio of company A showed an upward trend, and it had increased to 0.53 in 2023, which was 0.14 higher than that of 2021.
This paper analyzes the effectiveness of the accounting information management system constructed by integrating industry and finance. The essence of the trend analysis method is to compare and analyse the data in the financial statements of the enterprise for several consecutive years and summarize the changes in the company’s financial status and business performance on this basis. Take the financial status of Company A before and after 2018 as an example.The trend of Company A’s six-year developmental indicators is depicted in Figure 5.
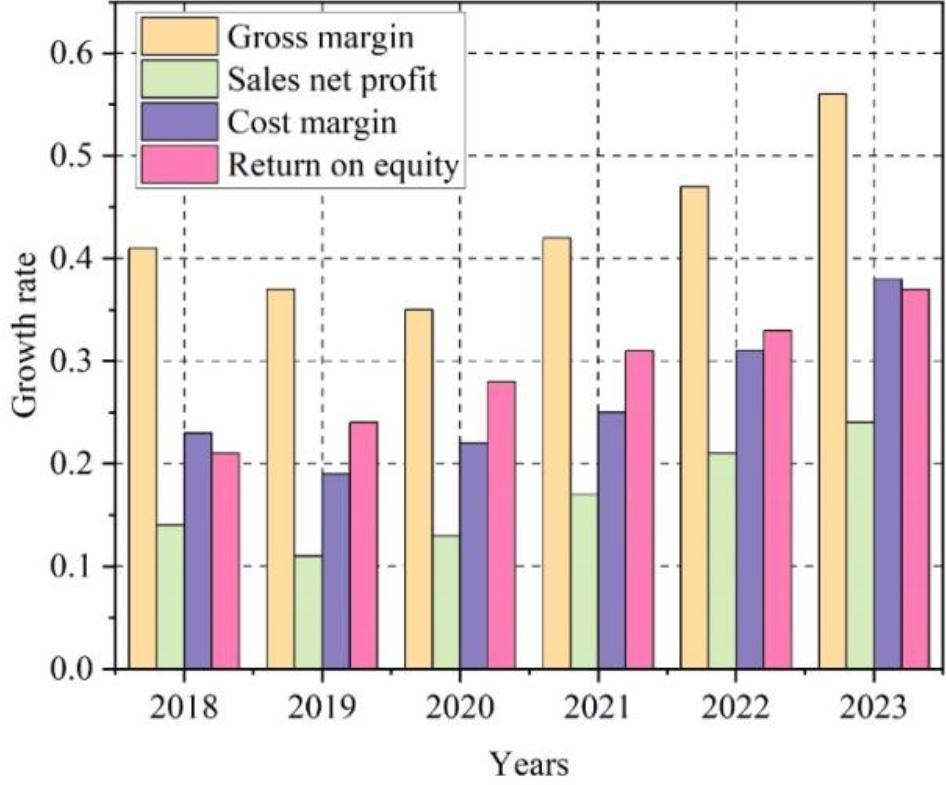
A company’s six year development indicators trend
After analyzing the trend of the company’s developmental indicators, it is not difficult to conclude that 2022 marks the key stage of the company’s development. Compared to the cost and expense utilisation in 2018, it increased by 8% in 2022. This is a direct indication that during the period from 2020 to 2023, Company A transformed and upgraded its development strategy. The construction of an information-based accounting management system based on the integration of industry and finance is the core factor of this strategic transformation.
During the period of 2022-2023, Company A’s gross profit margin on sales increased significantly to about 9%.Both the return on net assets and net profit margin on sales were on an upward trend, improving by 4% and 3%, respectively. The cost and expense margin fluctuated from 31% to 38%. This is a direct indication that after building the information management system based on the integration of industry and finance, Company A increased its profit and expanded its original sales scale, and also effectively controlled its costs to keep them down.
This section applies the industry-finance integration information management system to analyze the financial data of Company A. In order to test whether it can help managers to better manage the company and effectively reduce unnecessary costs.
Table 3 shows the results of the common benchmarking to analyze the main operating costs and profits. As can be seen from the table, the company’s cost of doing business ratio is generally on a downward trend, which is measured on the common benchmark of the main business income. In the three years from 2021 to 2023, the net profit and operating profit are on an upward trend, rising by 6.82% and 10.11%, respectively. This is a direct indication that when building an information management system based on the integration of industry and finance, Company A can effectively control costs and gain higher revenue, improving the company’s competitive advantage in the market and enhancing profitability.
| Project | Main business income | Main business cost | Operating profit | Net profit | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 12151652.62 | 7955686.97 | 2811892.42 | 1984364.87 | |
| 2022 | 12394002.21 | 7575214.15 | 3424462.81 | 2442857.84 | |
| 2023 | 12930587.60 | 7203630.35 | 4299420.38 | 2993431.03 | |
| Common reference | 2021 | 100% | 65.47% | 23.14% | 16.33% |
| 2022 | 100% | 61.12% | 27.63% | 19.71% | |
| 2023 | 100% | 55.71% | 33.25% | 23.15% | |
The purpose of this section is to analyze the effects of the business-financial integration of Company A using an information-based accounting management system. In this paper, a questionnaire survey is conducted on the first-level evaluation indicators of industry-finance integration proposed above, i.e., financial performance dimension, market performance dimension, decision-making and management dimension, innovation and learning dimension, and industry-finance integration situation dimension. The hierarchical analysis method described above was used to calculate the weights of each of the five evaluation indicators after 100 experts were invited to rate them. Figure 6 displays the weights of the evaluation indicators for each dimension in the information-based accounting management system.
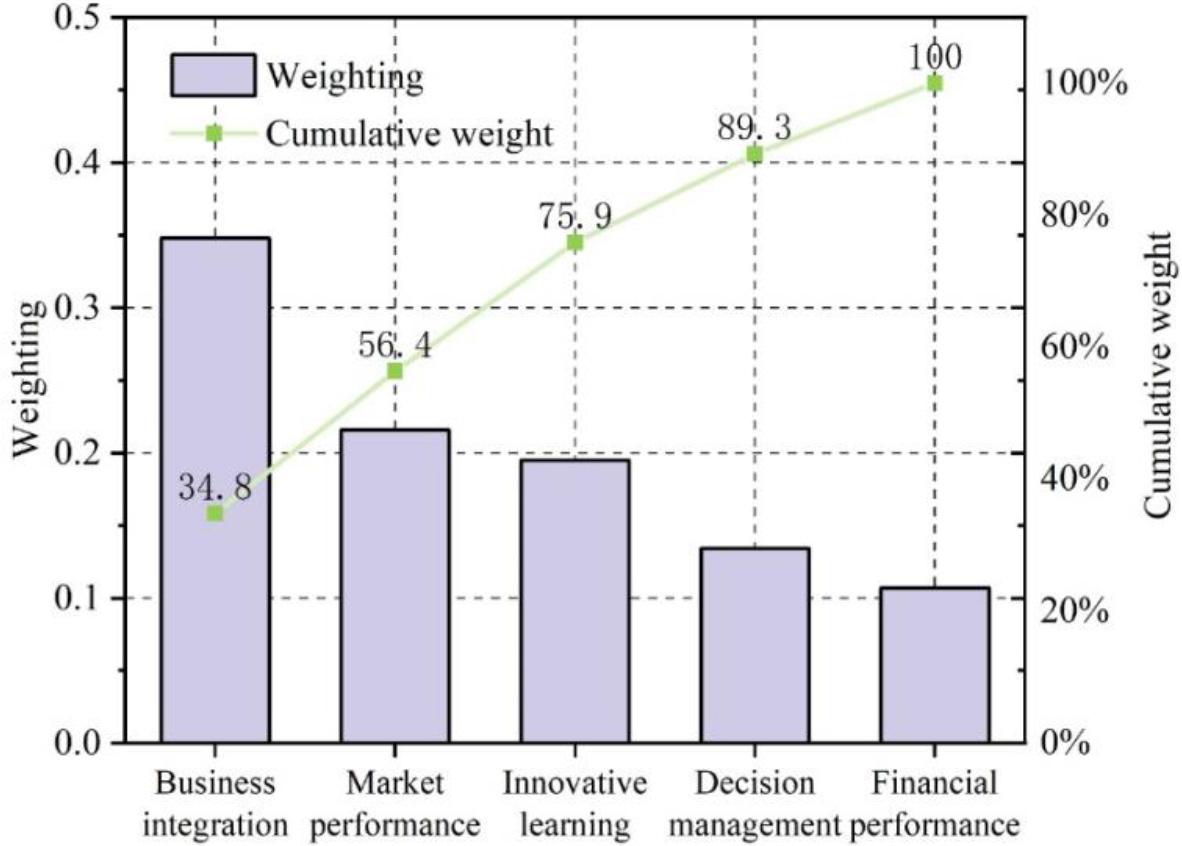
Index weight of each dimension
The data in the figure show that the weights of the dimension of business and financial integration and the dimension of financial performance are 34.8 per cent and 10.7 per cent, respectively, indicating that Company A pays more attention to business and financial integration when applying information-based accounting management system.
In addition, the above 100 experts fill in the questionnaire survey, respectively, the evaluation system, customer satisfaction, industry structural development, annual accurate poverty alleviation policy, environmental protection and scientific research input-output ratio, 5 indicators (in order to be recorded as indicators 1-5) to assess, through the numerical characteristics of the expected value of the Ex and entropy value of the En, the qualitative assessment of the 5 indicators into a quantitative representation. Figure 7 displays the expected value of the 5 indicators and the entropy value.
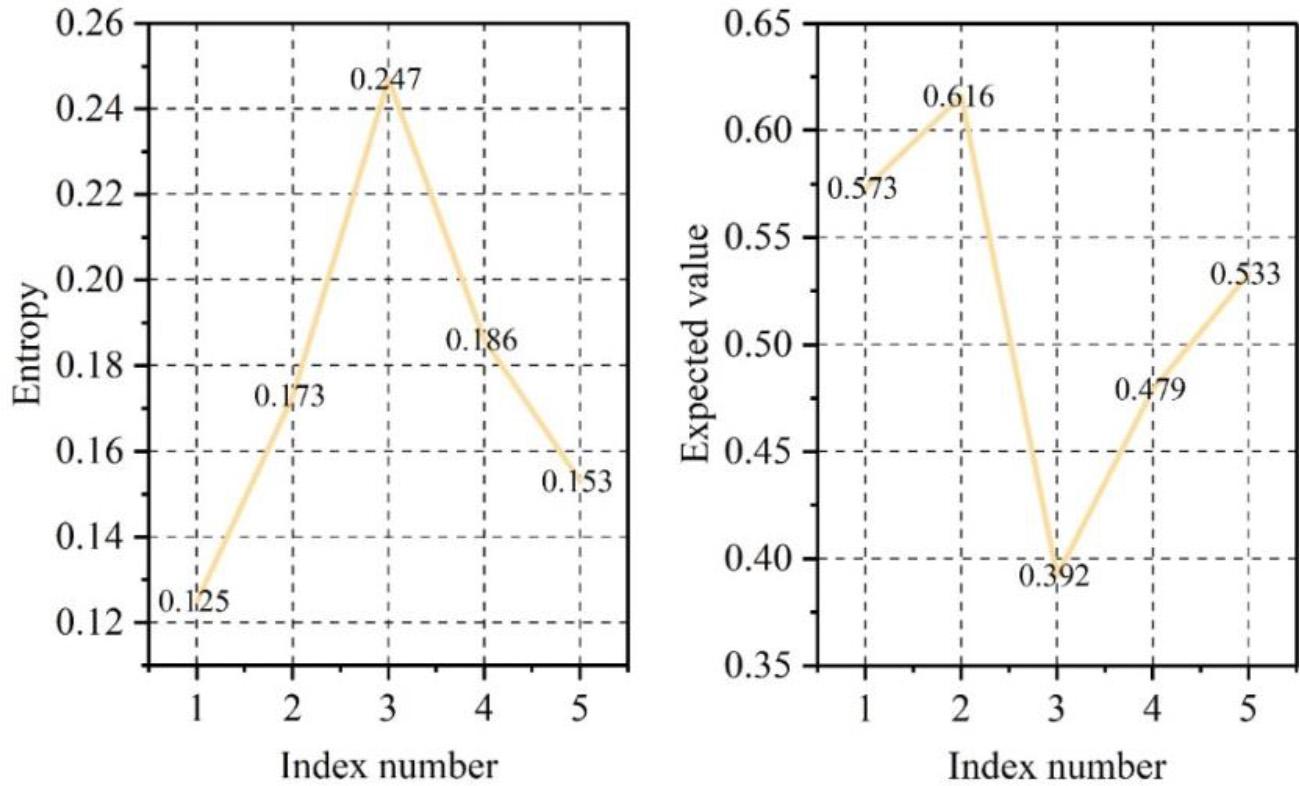
The expected value and entropy of the five indices
The numerical characteristic expectation value
The numerical eigenentropy
In the formula,
The figure shows that the expectation value for annual precision poverty alleviation is 0.392, and the entropy value is 0.247, both of which are low and have a high degree of dispersion. Therefore, in the process of industry-finance integration, we should focus on the annual precision poverty alleviation policy and distinguish the strengths and weaknesses so as to avoid losing much money for small reasons and ignoring the influence of other process results and other factors. In addition, the expected value of environmental protection situation and scientific research input-output ratio are lower than customer satisfaction and industry structural development, whose expected values are 0.479 and 0.533 respectively, and the entropy value is also at a medium level. It shows that industry-finance integration based on the information-based accounting management system prioritizes living in harmony with nature and avoiding obtaining benefits at the expense of the environment.The input-output ratio of scientific research is also crucial for promoting the integration of industry and finance.
This paper constructs an enterprise accounting information management system based on enterprise objectives and in the context of industry-finance integration. It was applied to listed company A in 2022, and the enterprise data of company A was visualised and analysed through data mining and OLAP multidimensional analysis, and the financial effect of this paper’s system for company A was evaluated using hierarchical analysis. After 2021, the operating indicators of Company A gradually increased. Until 2023, the inventory turnover ratio, accounts receivable turnover ratio, current asset turnover ratio, and total asset turnover ratio were 14.13, 11.25, 3.41, and 0.53, respectively.During the period of 2022-2023, the developmental indicators of Company A were improved.For example, the gross profit margin of sales increased by about 9%, while the cost and expense margin was stable at 31% to 38%. During 2021~2023, Company A’s cost of main business showed a downward trend, while the net profit margin and operating profit both increased, rising 6.82% and 10.11%, respectively. Applying the accounting information management system, Company A pays more attention to the integration of business and finance, which is weighted at 34.8%. In addition, Company A’s expectation for annual accurate poverty alleviation is only 0.392, and the entropy value is 0.247, i.e., the focus on poverty alleviation policy is weak.
Online and offline first-class course “Application of Excel in Accounting”.
