Entrepreneurial Project Management and Personal Career Growth Path Design Using the PDCA Cycle Model
Data publikacji: 17 mar 2025
Otrzymano: 06 lis 2024
Przyjęty: 12 lut 2025
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/amns-2025-0176
Słowa kluczowe
© 2025 Cui Zhang, published by Sciendo
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Cultivating talents needed for national construction is one of the key components of the college students’ innovation and entrepreneurship training program, which focuses on the cultivation of college students’ innovation and entrepreneurship ability, and puts forward higher requirements for the operation and management of the project [1-2]. Practice teaching is of great significance to the cultivation of students’ practical ability and innovation consciousness, and the effect of practice teaching is directly related to the high and low degree of the management level of the whole practice teaching [3-4]. Therefore, the use of a PDCA cycle theory as a quality management of the theoretical knowledge taught in the classroom is truly internalized into the practical ability of students and innovation ability, for practical teaching and practical teaching management has an important value [5-7].
PDCA method, also known as the “Deming cycle”, is a scientific procedure of total quality management, and the scientific procedure followed is one of the basic methods of project management, which is the abbreviation of the work cycle of “planning, execution, checking and processing” [8-10]. The PDCA method is cyclic in nature, but this cycle is not an unchanging cycle, but a kind of ladder-type spiral upward cycle, every cycle, the product quality and work efficiency will be improved by one step, and a new round of cycle management will be carried out with the main line of its cyclic upward [11-14]. Due to the uniqueness, temporary, target, life cycle and other distinctive project characteristics of college students’ innovation and entrepreneurship program and career growth planning, it has strong executability by drawing on modern project management concepts and methods for integrated planning [15-18]. The application of PDCA cycle theory in college students’ innovation and entrepreneurship training program can not only effectively expand the innovation and entrepreneurship project management methods, but also effectively promote the project quality management, and further improve the execution and innovation of college students’ innovation and entrepreneurship training program project team [19-21].
Based on the PDCA cycle model, this paper proposes entrepreneurial project management methods for the planning, implementation, inspection, and disposal stages respectively. Establish the evaluation index system containing entrepreneurial knowledge, entrepreneurial awareness, entrepreneurial ability, entrepreneurial goals and entrepreneurial spirit of PDCA entrepreneurial project management, after collecting data through questionnaires, extract the common factors by using factor analysis, further establish the regression model to obtain the regression equation between the evaluation effect of entrepreneurial project management and each common factor, and compare the index scores before and after the development of PDCA entrepreneurial project management mode , the application effect of PDCA entrepreneurial project management. At the same time, from the perspective of PDCA cycle theory, the theoretical framework of personal career growth path design is built, and relevant assumptions are put forward, with the help of empirical survey data, the elements of each link are evaluated through mean value analysis and variance test, and finally, combined with the structural equation model, the development of personal career growth path design is examined for its overall pattern and specific role path.
PDCA method, also known as the “Deming cycle”, is the scientific procedures of total quality management, the scientific procedures followed is one of the basic methods of project management, the connotation of the PDCA cycle, as shown in Figure 1, refers to the “Plan (Plan) - Implementation (Do) PDCA cycle connotation as shown in Figure 1, refers to “Plan (Plan) - Implementation (Do) - Check (Check) - Processing (Action)” work cycle of the abbreviation.
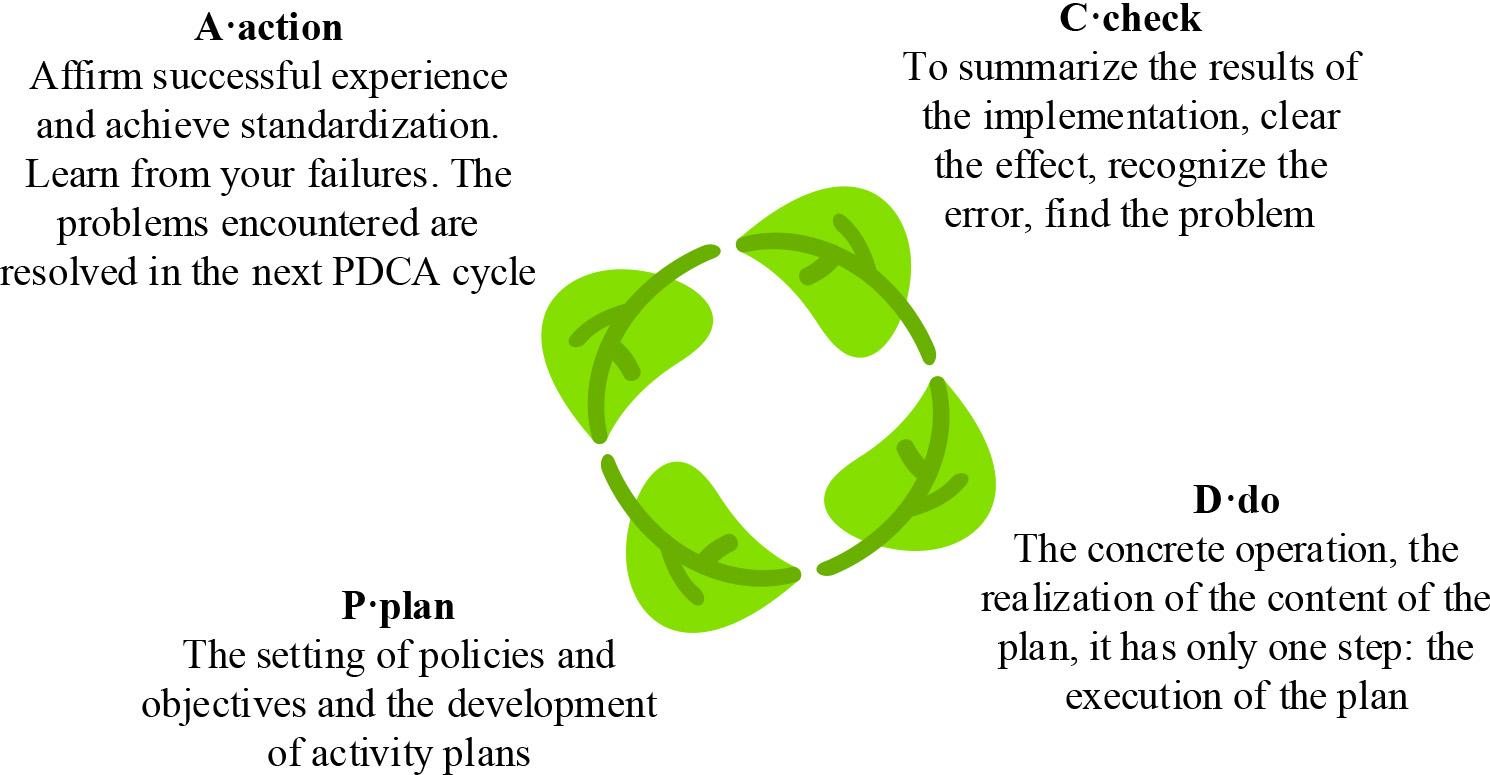
PDCA cyclic model
Project management includes three phases: project initiation, project implementation, and project acceptance, which can be further divided into several links, such as project initiation, evaluation, mid-term inspection, and final acceptance. In these processes, the PDCA method is specifically expressed as follows: P indicates that according to the project requirements, to determine the project objectives, content, implementation plan, etc., mainly embodied in the project initiation stage. D indicates that according to the project requirements and implementation plan, to carry out the corresponding activities, mostly embodied in the project implementation phase. C indicates that by means of self-examination of the project team, the faculty and departmental review and the school sampling inspection, to determine whether the implementation process of the project is in line with the requirements, mainly embodied in the mid-term inspection link and the final acceptance stage. The purpose of C is to determine whether the project implementation process meets the requirements through self-inspection by the project team, faculty review, and random inspection by the university, among other methods. It is mainly reflected in the mid-term inspection and the final acceptance stage.A is to take measures to correct the deviations of the project and prepare for the next higher stage of the PDCA cycle, which is mainly reflected in the treatment of the results of the project’s mid-term inspection and the final acceptance stage.
College students innovation and entrepreneurship training program since the start of work, many universities are actively exploring effective models and methods for this student research training, the following specific discussion of the PDCA cycle in the management of entrepreneurial projects.
According to the spirit of the documents of the Ministry of Education and the Provincial Department of Education, the academic affairs departments of each university will formulate the operation plan and methods suitable for the management of university students’ entrepreneurial projects, which can be completed in the following four steps:
Status survey. Accurately interpret the current objectives of talent training in the university, grasp the current hot issues, in the research of the knowledge accumulation of our students and the position of the level of scientific research training, and the feasibility of entrepreneurial projects to fully demonstrate. Analyze the key factors. Analyze the strengths and weaknesses of our students in the study of professional courses, as well as the interests and areas of concern in scientific research training, analyze some serious deficiencies revealed, and summarize the main factors that produce this result. Setting goals. Set the specific objectives of the university to carry out entrepreneurship programs for college students, the objectives can be qualitative or quantitative, or a combination of qualitative and quantitative, but the determination of the objectives must have a certain degree of feasibility and operability. Make plans. Based on the goals and desired effects, design the operation and management methods of the university entrepreneurship program that are appropriate for the university’s characteristics.
The second stage of the PDCA cycle is to formulate a specific and feasible course of action and lay out and execute it according to the preset goals and plans. For the entrepreneurship program, it is necessary to coordinate various internal factors, and the execution must be strong, so as to ensure that the entrepreneurship program and research work is carried out according to the planned progress and effective implementation. At this stage, in addition to looking at the overall situation of the University, it is more important to mobilize the implementation of the second-level faculties and departments in the management of entrepreneurship projects for students, not only to ensure that the local, but also to look at the overall situation, and ultimately to achieve the desired training results.
Whether the plans and programs developed for the management of entrepreneurship projects are effective and whether the objectives are achieved, these need to be checked and confirmed for effectiveness so that conclusions can be drawn that are sufficiently convincing. The expected goals are checked by comparing the completion of the entrepreneurship program in the current cycle to the pre-set target values.If the objectives have been confirmed, it means that the program has been implemented well. Otherwise, the program has failed and the objectives need to be reset to determine the best option.
This phase can be accomplished in the following two steps:
Setting standards. Plans, programs, and measures that have been examined and proved effective in the previous phase should be institutionalized and standardized in this phase, and promoted in subsequent management implementation. Summarize experience. The development and improvement of anything requires a process, which is impossible to summarize.The management level of entrepreneurial projects also requires the advancement of practice, constant summary of experience, and gradual improvement. Therefore, the PDCA cycle can not all solve all the problems in the management process of college entrepreneurship program, for the remaining problems, will automatically be transferred to the next PDCA cycle to solve, at the same time, but also for the next round of the PDCA cycle provides the basis for the next round of the PDCA cycle, and so on week after week, spiraling up.
The purpose of entrepreneurial project management is to stimulate and cultivate students’ sense of innovation and spirit of innovation, as well as entrepreneurial ability and management ability based on innovation. Based on the previous discussion of the application of the PDCA cycle model in entrepreneurial project management, this chapter assesses the effectiveness of the application of the PDCA entrepreneurial project management model by analyzing the degree of improvement of students’ knowledge and ability in entrepreneurial project management.
Five evaluation indicators of PDCA entrepreneurial project management were selected: entrepreneurial knowledge A, entrepreneurial awareness B, entrepreneurial ability C, entrepreneurial goals D, and entrepreneurial spirit E.
Entrepreneurial knowledge A dimension: enterprise management A1, laws and regulations A2, industry field A3, entrepreneurial policy A4 and business tax and insurance A5.
Entrepreneurial awareness B dimension: entrepreneurial desire B1, career B2, and opportunity sensitivity B3.
Entrepreneurial ability C dimension: problem identification C1, crisis management C2, independent learning C3, decision-making ability C4, communication ability C5 and leadership ability C6.
Entrepreneurial goals D dimension: goal establishment D1, goal management D2, and goal revision D3.
Entrepreneurial spirit E dimension: risk-taking spirit E1, responsibility E2, integrity E3 and self-confidence E4.
Based on the evaluation index system constructed in the previous paper, the Likert five-point method is used to assign values to the indicators, quantify the qualitative indicators, and lay the foundation for the subsequent empirical analysis. A one-year entrepreneurship program management based on the PDCA cycle model was carried out in a university, in which the survey targets were mainly general students (current entrepreneurship students, entrepreneurship graduates), entrepreneurship education experts (including innovation and entrepreneurship teachers in universities, entrepreneurship competition evaluation experts, entrepreneurship celebrities).
A total of 353 questionnaires were distributed in this survey, and a total of 305 questionnaires were recovered, with a recovery rate of 86.40%. After eliminating the waste papers, 274 valid questionnaires were obtained, and the validity rate of the questionnaire was 89.84%. The questionnaire is both reliable and valid.
Factor analysis was first used to downscale the collected indicator data, and then multiple regression analysis was used to establish the model between the entrepreneurial project management effect and each evaluation factor, and then to obtain the entrepreneurial project management effect.
The focus of factor analysis is on the internal interrelationships between variables, using multiple composite factors that are independent of each other to represent the underlying bodies of the observed data.These composite factors effectively summarize the main information of the original variables, and they also replicate the relationship between the original variables and the factors. Among them, the original variable is observable and is a manifest variable. The composite factor is a latent variable that cannot be observed.
The mathematical model for factor analysis is as follows:
The general model is:
In Eqs. (1) and (2), y = (
In Equation (3),
Regression analysis is a very important branch of statistics. It is based on probability theory and mathematical statistics, and has rapidly developed as a more applied scientific method.Linear regression is categorised into univariate linear regression and multiple linear regression. One-dimensional linear regression model is a linear regression problem in which the dependent variable is related to only one independent variable. However, in many practical problems, the univariate linear regression model is only a special case of regression analysis, which is usually the result of simplified consideration of many factors that affect a certain phenomenon.In this paper, a multiple linear regression model is used to examine the relationship between the effects of two or more independent variables on the change in the quantity of a dependent variable.
The general form of the multiple linear regression model is as follows:
If given a set of
For random errors
When considering a specific practical problem, if monitoring data (
Order:
Then model (6) is:
Call (9) the matrix form of the multiple linear regression model.
To facilitate the estimation of the parameters in the model, the following basic assumptions are made for the regression equation (6):
Assumption 1, the independent variable Assumption 2, which satisfies the Gauss-Markov condition (G-M condition), i.e:
Assumption 3, the normal distribution is assumed:
Assumption 1 states that the independent variables in the regression problem are deterministic, and Assumption 2 states that the mean of the random error is zero and that there is no systematic error in the monitored values. The covariance of the random error term
Under the condition that the above three assumptions are satisfied, the matrix form of the multiple regression model (9) is written in the form:
If the multiple linear regression model is to be utilized for analysis and prediction, the model parameters need to be estimated first
First, a few definitions are given.
The deviation of the sample monitoring value (
Sum of squared deviations:
The so-called Least Squares Estimate (LSE)
In this case,
The above process can be realized by the method of finding the extremes in multivariable calculus, and the specific calculation will not be repeated in this paper. The least squares estimation coefficient formula is:
Once the estimates of the regression parameters are obtained, the empirical regression equation represented by equation (5) can be used to predict the dependent variable
In this paper, we intend to extract the common factors of entrepreneurial knowledge, entrepreneurial awareness, entrepreneurial ability, entrepreneurial goal and entrepreneurial spirit by using factor analysis to represent the full meanings of the corresponding secondary indicator system, so as to achieve the purpose of downgrading the dimensionality while ensuring the scientificity of the research.
The results of factor analysis are shown in Table 1. A male factor with eigenvalue above 1 was extracted after factor analysis of the second-level indicators A1~A5, and the explanatory strength of the male factor for all the indicators reached 78.259%. Similarly, the strength of explanation of the other four public factors for the indicators is 81.765%, 79.825%, 77.547%, and 78.867%, respectively. From the matrix of component score coefficients, the formula for the calculation of the public factors can be obtained:
A=0.236*A1+0.272*A2+0.306*A3+0.237*A4+0.246*A5 B=0.425*B1+0.477*B2+0.403*B3 C=0.379*C1+0.368*C2+0.355*C3+0.348*C4+0.385*C5+0.363*C6 D=0.389*D1+0.436*D2+0.424*D3 E=0.305*E1+0.322*E2+0.341*E3+0.325*E4 Results of factor analysis
Total variance interpretation
Initial eigenvalue
Extracting the load of the load
Component score coefficient
Total
Variance%
Cumulate%
Total
Variance%
Cumulate%
A1
2.207
78.259
78.259
2.207
78.259
78.259
0.236
A2
0.608
10.858
89.117
0.272
A3
0.504
6.589
95.706
0.306
A4
0.477
3.498
99.204
0.237
A5
0.257
0.796
100.000
0.246
B1
1.856
81.765
81.765
1.856
81.765
81.765
0.425
B2
0.614
12.537
94.302
0.477
B3
0.251
5.698
100.000
0.403
C1
2.577
79.825
79.825
2.577
79.825
79.825
0.379
C2
0.822
7.722
87.547
0.368
C3
0.630
5.534
93.081
0.355
C4
0.559
3.564
96.645
0.348
C5
0.312
2.309
98.954
0.385
C6
0.279
1.046
100.000
0.363
D1
1.778
77.547
77.547
1.778
77.547
77.547
0.389
D2
0.875
15.348
92.895
0.436
D3
0.362
7.105
100.000
0.424
E1
2.802
78.867
78.867
2.802
78.867
78.867
0.305
E2
0.823
11.324
90.191
0.322
E3
0.555
7.339
97.530
0.341
E4
0.213
2.470
100.000
0.325
The evaluation values of entrepreneurial knowledge, entrepreneurial awareness, entrepreneurial ability, entrepreneurial goals, and entrepreneurial spirit can be obtained by bringing the data of secondary indicators into the above formula.
The factor analysis method is limited to extracting the common factor of the index system and cannot evaluate the impact of PDCA entrepreneurship project management. Therefore, this paper further conducts regression analysis, constructs regression model, establishes assessment regression equation, and the regression results of each variable are shown in Table 2. The F value of the regression model is 26.574, and the significance is 0.000, which indicates that the data of each variable is statistically significant, the regression model has practical value, and the adjusted R2 of the regression model is 0.663, which indicates that the regression model fits the goodness of fit better.
Regression result of variables
| Nonnormalized coefficient | Normalized coefficient | t | Significance | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard error | |||||
| Constant | 0.882 | 0.291 | 2.359 | 0.006 | |
| 0.152 | 0.127 | 0.215 | 3.821 | 0.002 | |
| 0.180 | 0.037 | 0.178 | 2.551 | 0.008 | |
| 0.314 | 0.075 | 0.338 | 1.383 | 0.001 | |
| 0.077 | 0.054 | 0.042 | 3.751 | 0.004 | |
| 0.082 | 0.063 | 0.021 | 2.668 | 0.005 | |
| Model | Sum of squares | Df | Mean square | F | Significance |
| Regression | 81.789 | 5 | 17.754 | 26.574 | 0.000 |
| Residual error | 124.726 | 221.479 | 0.301 | ||
| Total | 254.326 | 265.808 | |||
| Adjusted |
S.E. | ||||
| 0.855 | 0.785 | 0.663 | 0.854 | ||
The significance levels of variables A~Variable E are all above 0.01, and the regression equation is constructed as:
The scores of the students’ dimensional variables before and after the implementation of PDCA entrepreneurship program management in the sample universities were calculated, and the evaluation results of entrepreneurship program management are shown in Figure 2. After the implementation of the entrepreneurial project management model based on the PDCA cycle model, the sample students improved their entrepreneurial knowledge, entrepreneurial awareness, entrepreneurial ability, entrepreneurial goals, and entrepreneurial spirit by 18.50% to 47.35%. According to the regression equation, the comprehensive evaluation scores before and after the implementation of PDCA entrepreneurship project management were 3.13 and 3.98 respectively, with an overall improvement of 27.16%, indicating that the entrepreneurship project management mode based on the PDCA cyclic model can improve the entrepreneurial knowledge and innovation ability of entrepreneurship project training students, showing good application effects.
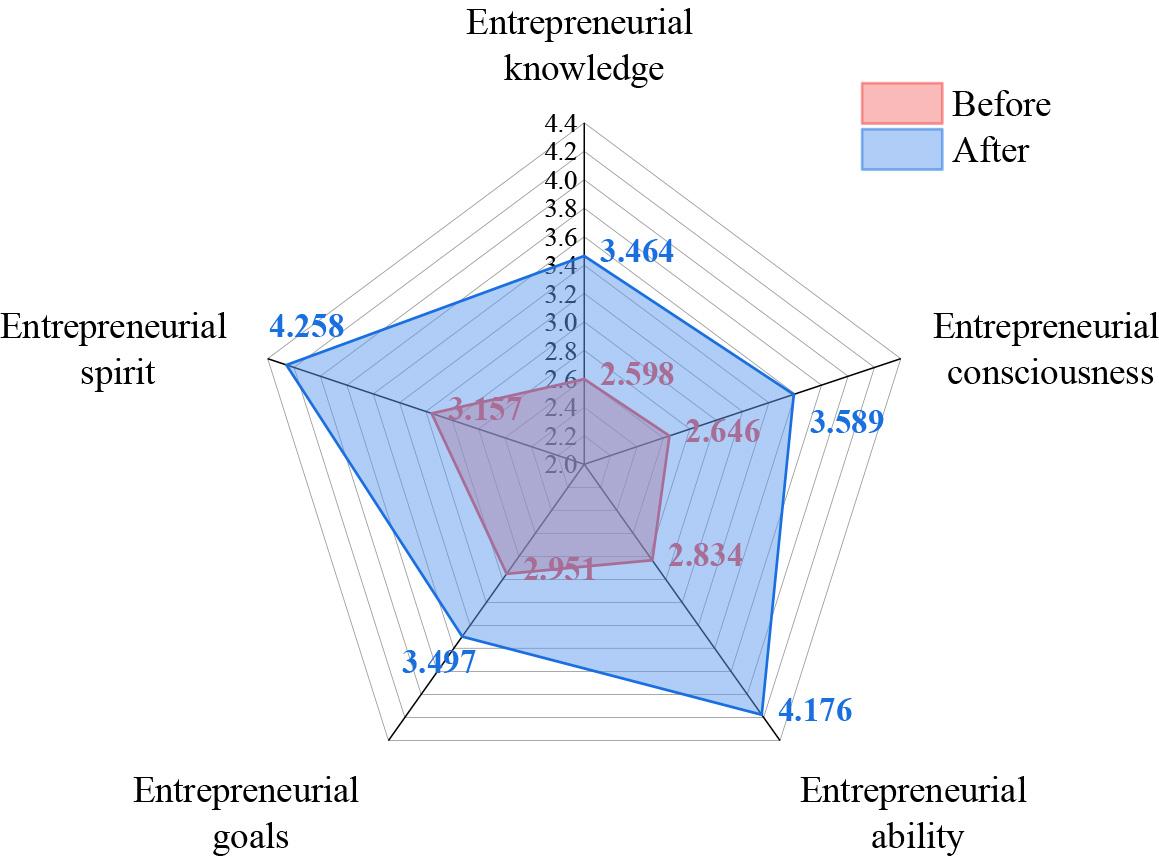
Evaluation of venture project management
The current employment situation has presented new challenges for talent cultivation in colleges and universities. Through the previous analysis, entrepreneurial project management based on the PDCA cycle model can promote students’ innovation and entrepreneurship ability, and this chapter introduces the PDCA cycle model into the design of students’ personal career growth path in colleges and universities, and utilizes structural equations to construct a model to explore the various links in the process of students’ personal career growth path.
The modern view of improvement is that the PDCA cycle can be expanded into planning decision-making (resource allocation decisions), implementation design (implementation pathways and strategies), process control (monitoring and management of implementation), and outcome assessment (evaluation cycle of improvement).The introduction of the PDCA cycle into the design of personal career growth paths helps to monitor the level of total quality management of personal career growth paths at the present stage from a holistic point of view, and to discover room for improvement of personal career growth paths in schools. The introduction of PDCA cycle into the design of personal career growth path helps to monitor the overall quality management level of personal career growth path at this stage from a holistic perspective, and explore the room for improvement of personal career growth path in school.
The specific connotations of the PDCA cycle introduced into the design of the personal career growth path include: resource allocation in the field of school personal career growth education (planning), internal and external implementation strategies of the school personal career growth education support system (execution), monitoring and control of the school personal career growth education and cultivation process (monitoring), and the evaluation and improvement of the students’ personal career growth planning ability (improvement). Finally, a step-by-step design path is constructed that includes the four links mentioned above.
The PDCA-based personal career growth path design framework is shown in Figure 3. First of all, at the level of program decision-making, resource input is an important characterization of the school’s attention to resource allocation, and the school must make sense of all the resources that can be utilized and expanded to carry out personal career growth education at present. The core elements of resource inputs are identified as institutional settings, full-time teachers, curriculum materials, financial allocations, and information resources.
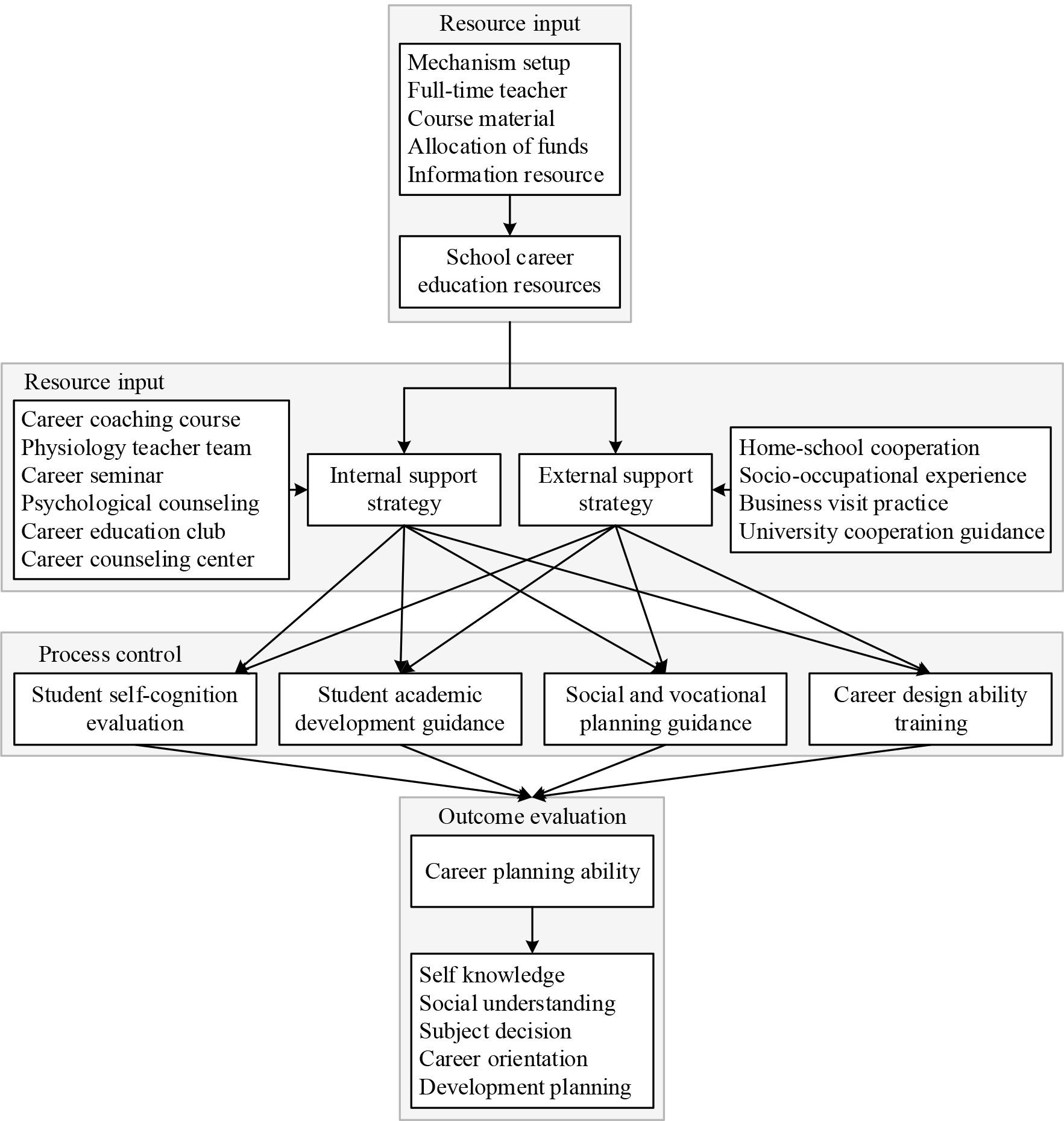
Based on PDCA’s personal career growth path design framework
Secondly, in the stage of execution and implementation, it is necessary to do a good job in the delivery and implementation of resource inputs, i.e., to further refine the support strategy, formulate the nodal plan, and strengthen the control of the link. According to the spatial dimension of the implementation of personal professional growth education, the school’s implementation strategy is divided into internal support and external support. Internal support includes counseling courses, teacher teams, special lectures, psychological counseling and tutoring, educational clubs, and counseling centers. External support includes homeschool cooperation and co-education, social and vocational experience, business visits and practice, and collaborative guidance from colleges and universities.
Again, from the elements of process control, the measurement indicators include students’ self-knowledge evaluation, academic development guidance, social career planning, and career design ability.
Finally, at the level of outcome assessment and improvement, students’ career planning ability is taken as a core indicator of the quality assessment and improvement of personal career growth education, which is subdivided into five aspects, including self-knowledge, social understanding, disciplinary decision-making, career orientation, and development planning.
Based on the theoretical framework, this study proposes the following research hypotheses:
H1: Personal career growth educational resources will positively influence internal and external support strategies for personal career growth paths, and resource investment will influence external support strategies to a higher degree. H2: School internal and external support strategies will positively affect the process control of personal career growth path to varying degrees. H3: Elements of process control will positively promote students’ career planning skills to varying degrees.
The students of the same university were selected as subjects, 357 student questionnaires were distributed, 311 questionnaires were recovered, and questionnaires that took shorter than 3 minutes to fill in, and the options were highly consistent were excluded, resulting in 293 valid samples, and the validity rate of the questionnaires was 94.21%.
In terms of the score situation and difference analysis of the assessment subsystem, mean value analysis and ANOVA test were performed.In terms of the personal career growth path design test, structural equation modeling (SEM) was used to explore the influential links in the student’s personal career growth path.
Variables that are not directly measurable are often encountered in research, and the use of structural equation modeling can be used to verify the causal relationship between multiple variables, and the use of observable variable data and theoretical structural modeling can be done to measure the variables that are not directly observable. Specifically, the model consists of two aspects: the structural model and the measurement model.
Structural models evolved from path analysis models. In the path analysis model, variables that can be directly observed are referred to as explicit variables, while variables that cannot be directly observed are referred to as latent variables. A single arrow pointing represents a causal relationship between variables, from the cause variable to the effect variable.A double arrow pointing indicates a correlation between the variables, but the causal relationship is not yet clear.Path coefficients from path analysis models are basically standardized regression coefficients that can be utilized to measure the correlation between two variables. Structural models are mainly used to analyze the “causal effect” between latent variables and are defined as follows:
Let
The measurement model is partially transformed from the factor analysis model. Factor analysis models are characterized by the downscaling of multiple known variables into a small number of major factors, and the major factors are orthogonal to each other, with each factor being a linear combination of known variables. The measurement model of structural equations is analyzed from the theory of economics to derive some kind of correlation existing between the variables, and the theoretically derived correlation is used as the basis for validation factor analysis. In order to facilitate model identification, it is necessary to set a specific unit of measurement, usually using the fixed-load method and the fixed-variance method.The fixed-load method involves setting a specific load to a fixed value, typically 1, while the fixed-variance method involves setting a specific variance of a variable to a fixed value, typically 1.
In measurement modeling, external explicit variables are linked to corresponding latent variables, and validated factor analysis is typically used to test the factor structure of latent variables. It is defined as:
The main estimation methods for structural equation modeling include two types of frequency school methods (e.g., great likelihood estimation) and Bayesian methods Using the Bayesian method to analyze structural equations, the a priori distributions of unknown parameters and latent variables can be determined by using existing theories and existing research results. Using Bayesian equations, combining the prior distributions with the data likelihood function, the posterior distributions of the unknown parameters and latent variables can be derived, and then the posterior distributions are iteratively extracted using the Markov Chain Monte Carlo algorithm with the means, confidence intervals, and other statistics of the posterior distributions.
Bayes’ theorem is the core of the Bayesian approach. Suppose the researcher wishes to estimate the unknown parameter (
The student evaluation of each element of the personal career growth path based on the PDCA cycle model was obtained by summing and averaging the values of the measurement questions for each element and analyzing the descriptive statistics, and the scores of each index are shown in Table 3, with *** indicating p < 0.001.
The scoring of all elements of the growth path
| Dimension | Mean | S.D. | Difference test | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resource input | Career education resources | 3.356 | 0.903 | F=10.582*** |
| Execution strategy | Internal support strategy | 3.863 | 0.641 | F=8.628*** |
| External support strategy | 3.467 | 0.784 | F= 4.651 | |
| Process control | Student self-cognitive evaluation | 4.283 | 0.814 | F= 5.177*** |
| Student development guidance | 4.072 | 0.533 | F=6.521*** | |
| Social career planning guidance | 3.858 | 0.614 | F=8.169*** | |
| Career design ability culture | 3.663 | 0.573 | F=7.172*** | |
| Result assessment | Career planning ability | 3.325 | 0.765 | F= 2.518*** |
In the four dimensions of resource input, implementation strategy, process control and outcome assessment, the scores of each dimension are above 3, which is in the middle-upper level, indicating that the PDCA-based personal career growth pathway design of the sample colleges and universities is better in cultivating students’ career planning ability, but there is still some room for improvement. At the level of implementation strategies, the score of the on-campus support strategy is higher than the score of the off-campus support strategy at the level of 11.42%, which means that the school adopts more internal support methods such as on-campus courses, expert lectures, and counseling and tutoring for students’ personal career growth education.
At the level of process control, in order of the mean score, the evaluation of students’ self-knowledge (4.283), the guidance of students’ academic development (4.072), the guidance of socio-vocational planning (3.858), and the cultivation of career design skills (3.663) were ranked in order of magnitude. This shows that the school pays more attention to students’ self-knowledge and academic development guidance.
Validated factor analysis (CFA) was used to test the questionnaire’s topic reliability, component reliability, and convergent validity. The results of the validated factor analysis are shown in Table 4, *** denotes p < 0.001. The lowest standardized factor loadings of the questions for each dimension in all measurement models, Std, were greater than 0.64, the squared values of the multiple correlations, SMC, were greater than 0.43, the CR values of the constitutive reliabilities averaged around 0.8-0.9, and the convergent validity (AVE) was around 0.6-0.7, and all of the indexes were better than the econometric All indicators are better than the econometric values. Thus, the model is reliable and valid, and the measurement indicators can more accurately depict the characteristics of latent variables and aid in the subsequent SEM analysis.
Analysis of the model verification factor of the structural equation
| Dimension | Sth | SMC | CR | AVE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Career education resources | 0.646~0.869*** | 0.458~0.778 | 0.917 | 0.752 |
| Internal support strategy | 0.663~0.873*** | 0.511~0.861 | 0.851 | 0.678 |
| External support strategy | 0.655~0.903*** | 0.617~0.787 | 0.885 | 0.779 |
| Student self-cognitive evaluation | 0.649~0.916*** | 0.434~0.729 | 0.896 | 0.757 |
| Student development guidance | 0.731~0.883*** | 0.608~0.809 | 0.909 | 0.763 |
| Social career planning guidance | 0.665~0.942*** | 0.569~0.775 | 0.943 | 0.669 |
| Career design ability culture | 0.722~0.929*** | 0.539~0.833 | 0.848 | 0.685 |
| Career planning ability | 0.641~0.849*** | 0.467~0.857 | 0.867 | 0.672 |
In this study, the fit indices of the structural equation model (
The path coefficient test of structural equation modeling is shown in Table 5, with ** denoting p < 0.01 and *** denoting p < 0.001. Firstly, the educational resources for personal professional growth have a significant positive effect on support strategies both inside and outside the school, and to a greater extent on support strategies outside the school, with path coefficients of 0.615 and 0.206 (p < 0.01) on the effect of internal and external support strategies, respectively.
The path coefficient test of the structural equation model
| DV | IV | Estimate | S.E. | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Career education resources | Internal support strategy | 0.206 | 0.064 | ** |
| External support strategy | 0.615 | 0.051 | *** | |
| Internal support strategy | Student self-cognitive evaluation | 0.524 | 0.059 | *** |
| Student development guidance | 0.331 | 0.088 | *** | |
| Social career planning guidance | 0.191 | 0.097 | *** | |
| Career design ability culture | 0.255 | 0.051 | *** | |
| External support strategy | Student self-cognitive evaluation | 0.352 | 0.072 | *** |
| Student development guidance | 0.284 | 0.081 | *** | |
| Social career planning guidance | 0.495 | 0.087 | *** | |
| Career design ability culture | 0.202 | 0.087 | *** | |
| Student self-cognitive evaluation | Career planning ability | 0.529 | 0.091 | *** |
| Student development guidance | 0.448 | 0.066 | *** | |
| Social career planning guidance | 0.527 | 0.053 | *** | |
| Career design ability culture | 0.428 | 0.061 | *** |
Second, both internal and external support strategies significantly and positively influence the practice process to varying degrees. The internal support strategy had the highest degree of influence on self-perception evaluation with a path coefficient of 0.524 (p < 0.01). The external support strategy had the highest degree of influence on social career planning guidance, with a path coefficient of 0.495 (p < 0.001).
Finally, the practical control of personal career growth path had a significant positive effect on improving students’ career planning skills. Among them, self-perception evaluation and social career planning guidance have the highest degree of influence on students’ career planning ability, with path coefficients of 0.529 (p < 0.001) and 0.527 (p < 0.001), respectively. Hypotheses H1~H3 were all verified.
This paper constructs an entrepreneurial project management model based on the PACD cyclic model, and analyzes its application effect after constructing the PACD entrepreneurial project management evaluation model by combining factor analysis and multiple regression analysis. At the same time, the PACD cycle model is used in the design of personal career growth path for college students, establishing a theoretical framework, evaluating each element of the path, and combining with the structural equation modeling to explore the various aspects of personal career growth education.
Through the construction of regression equation, the quantitative relationship between PDCA entrepreneurial project management and each variable is established: the assessment effect of PDCA entrepreneurial project management = 0.152* entrepreneurial knowledge + 0.180* entrepreneurial awareness + 0.314* entrepreneurial ability + 0.077* entrepreneurial goal + 0.082* entrepreneurial spirit + 0.882. After the implementation of PDCA entrepreneurial project management, the sample students improved 27.16% in innovation and entrepreneurship knowledge and ability as a whole, with the most significant effect of entrepreneurial ability, reflecting the good effect of entrepreneurial project management based on PDCA cycle model.
The sample colleges and universities have scores of greater than 3 in the four segments of the students’ personal career growth path based on the PDCA cycle model, namely, resource input, implementation strategy, process control and outcome assessment, which are located above the medium level. The hypotheses made in this paper were all tested (p < 0.01), i.e., educational resources in the personal career growth path have a significant positive effect on the internal and external support strategies, the internal and external support strategies positively and significantly affect the practice process, and the control of the practice process positively and significantly affects the enhancement of the students’ career planning ability.
The research and analysis proved that applying the PDCA cycle model to entrepreneurship project management and personal career growth path design is conducive to promoting the development of students’ innovation and entrepreneurship ability and the development of students’ career planning ability, which in turn improves the comprehensive level of talent cultivation of colleges and universities.
This research was supported by the Henan Provincial Private Education Association: Research on talent training mode of Private undergraduate universities in Henan Province under the perspective of special creation and integration (No.: HNMXL20230084).
