Study on the International Promotion Path of Fujian’s Intercultural Communication Strategy under the Belt and Road Framework Based on Big Data
Data publikacji: 17 mar 2025
Otrzymano: 16 paź 2024
Przyjęty: 10 lut 2025
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/amns-2025-0158
Słowa kluczowe
© 2025 Yan Zhuang et al., published by Sciendo
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Historically, a large number of Fujianese people have migrated overseas, and the culture of the Fujian region has spread far and wide to Taiwan, Southeast Asia, Japan, the United States and other places. Intercultural communication is conducive to enhancing cultural diversity, promoting the continuous integration of cultures, and reducing conflicts and contradictions caused by cultural differences, thus strengthening the exchanges between overseas Chinese and overseas Chinese and contributing to the development of the regional economy as well as the harmony of the society, and under the promotion of the new era, intercultural communication in Fujian has ushered in a new height [1-4].
With the promotion of the “One Belt, One Road” initiative, cultural exchanges and communication have become an important aspect of promoting international cooperation. Intercultural communication plays an important role in it. It will help promote mutual understanding and respect among different cultures, promote harmonious coexistence, and also help promote economic, commercial and political interactions within the “Belt and Road” [5-8]. First of all, cross-cultural communication can promote mutual understanding and respect among different cultures. In the process of mutual communication and understanding, people can better understand the differences in ideas, values and lifestyles between different cultures [9-10]. This can reduce misunderstanding and prejudice between different cultures, as well as avoid some cultural conflicts and frictions. At the same time, the interaction of intercultural communication can also promote the diversification of cultural development and learning so as to enrich people’s thoughts and culture [11-13]. Secondly, intercultural communication can help promote economic, commercial and political interaction within the Belt and Road. By means of cross-cultural communication, enterprises can better carry out their international market strategies and increase their brand awareness and market share [14-17].
Literature [18] based on the “Belt and Road” discusses the opportunities and challenges of cross-cultural communication of traditional folk dances in Fujian, communication paths and innovative communication strategies, and it is found that Fujian folk dances have distinctive national characteristics, and their communication forms should be innovative and pay attention to cultural differences and barriers. Only by constantly showing its artistic value and realizing cultural integration can it meet the needs of cross-cultural communication. Literature [19] discusses the significance of cross-cultural communication between China and the countries along the route under the background of “One Belt, One Road” and puts forward strategies to deal with the obstacles exposed in the process so as to strengthen the cultural exchange and the connection between the people of China and the countries along the route. Literature [20] points out that the Belt and Road Initiative brings misunderstanding and friction due to cultural differences. Challenges such as cross-cultural identity and culture shock that may be encountered in the management of international students are examined, aiming to provide a reference for solving cross-cultural problems such as cultural identity barriers. Literature [21] describes the process of cross-cultural exchanges of “One Belt, One Road” from the perspectives of cultural values and cross-cultural relations. It also discusses the future issues related to the Belt and Road. Literature [22] emphasizes the positive impact of the “One Belt, One Road” policy and the cross-cultural communication strategy of Chinese film culture in this context, aiming to promote the sustainable development of Chinese film culture overseas through the “One Belt, One Road” opportunity of the times. The aim is to promote the sustainable development of Chinese movie culture overseas through the opportunity of “Belt and Road”. Literature [23] describes the innovative strategy of promoting the excellent folk dance culture through the “Belt and Road” strategy, which is realized through the establishment of this cultural dissemination system, the improvement of the professional talent training mode, and the full exploration of folk dance resources based on the global vision. Literature [24] affirms the importance of cross-cultural communication and analyzes the difficulties encountered in the process of cross-cultural communication in the context of China’s “One Belt, One Road” and its coping strategies in order to promote the smooth progress of the “One Belt, One Road”. Literature [25] takes Qilu culture as the research object, explores its connotation and value in cross-cultural communication in the new period, and examines the feasible path of cross-cultural communication of Qilu culture by combining the characteristics of film and television culture and its development advantages under the “Belt and Road”. Literature [26] describes the communication strategy of Chinese folk culture under the background of “One Belt, One Road”, discussing the characteristics of folk culture, the current development situation, the significance of cross-cultural communication, the existing problems, and the communication strategy, etc. The study also examines the feasible path of cross-cultural communication in Qilu culture. Literature [27] shows that the development of the “One Belt, One Road” initiative has brought a certain degree of cultural risk. Therefore, it is emphasized that in the context of the times, in addition to paying attention to “cultural dissemination” and “cultural export”, it is also necessary to pay attention to cultural security and cross-cultural communication security construction. Literature [28] appreciates the positive impacts of the “Belt and Road” strategy, such as “eliminating prejudice” and “enhancing political mutual trust”, and tries to analyze It also tries to analyze the problems and coping strategies in cross-cultural communication in the context of “Belt and Road”, aiming to promote the better development of “Belt and Road”.
In this paper, after the preliminary study of intercultural communication strategy in Fujian Province, the Decision Laboratory Analysis Method (DEMATEL) and Interpretative Structural Modelling (ISM) are combined to construct the DEMATEL-ISM model, which is used to explore the influencing factors of the international promotion of intercultural communication strategy in Fujian Province. The DEMATEL method establishes a comprehensive influence matrix, based on which the influence, influenced, centred, and cause degrees of the influence indicators are calculated and then transformed into the reachability matrix in the ISM model, which divides the influencing factors into different levels, and constructs a multilevel progressive explanatory structural model in order to visually explain the influencing relationships of the factors in the international promotion of Fujian’s cross-cultural communication strategy. Based on the conclusions obtained, corresponding international promotion strategies for intercultural communication strategies are proposed.
Strengthen the integration and expression of cultural elements
In the process of cross-cultural communication, Fujian should deeply explore the unique elements of local culture and show the charm of Fujian culture. Through the combination of tradition and modernity, local culture and international elements should be organically combined. Systematically sort out Fujian’s traditional cultural resources, including historical allusions, ethnic customs, artistic expressions, etc., to form a rich library of cultural materials, which can provide continuous cultural nourishment for sports events. Distil representative cultural symbols and elements from Fujian traditional culture and integrate them into all aspects of cross-cultural communication so as to display the unique flavor of Fujian.
Enhance the internationalisation of language services
Fujian should formulate a multilingual communication strategy and provide language services for different countries and regions. Translation and localisation, etc., ensure accurate communication and wide coverage of cultural information. Provide multilingual services targeting audiences in different countries and regions, including common languages such as English, French, and Spanish, as well as some niche languages. Through multilingual services, we will address the needs of various audiences and enhance the international impact of Fujian culture. Provide customized language services based on the cultural background and language habits of various audiences.
Strengthen International Exchange and Co-operation
Organise cross-cultural exchange activities, such as cultural forums and cultural exhibitions, to provide a platform for cultural figures from different countries to communicate and collaborate, and to promote cross-cultural exchange and dissemination. Actively participate in international cultural exchange activities to showcase the charm and strength of Fujian culture. In any cross-cultural communication, it is necessary to treat the content being communicated and the recipients of the communication with a peaceful mindset. To be ashamed of oneself, to be self-deprecating, or to be above the recipients implies ignorance and parochialism.
Fujian Province is a large resource province of intangible cultural heritage, and the dissemination of non-heritage culture is an important element in its cross-cultural communication strategy. “The traditional non-heritage narrative mainly relies on mainstream media to popularize non-heritage knowledge to audiences, and the emergence of new social media such as short videos, live broadcasts and games provides new carriers for non-heritage narratives and brings new experiences to audiences.” The audience has moved from the big screen to the small screen and cell phone, which means that the dissemination of non-legacy culture is no longer limited to a single platform and a single group of people but a diversified platform the dissemination of non-legacy culture has been established on the mobile terminal.
China’s non-legacy has taken on the mission of “continuing cultural traditions” given by the times, and it should adhere to the principle of “going out”, strengthen the exchanges of non-legacy culture, and spread the essence of traditional Chinese culture to the world. The Fujian Provincial Art Museum (Fujian Intangible Cultural Heritage Protection Centre) has organized a number of exhibitions and exchanges, including the World Horticultural Expo “Fujian Day”, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs’ global promotional activities - “China in the New Era: Sailing on the Silk Road in Eco-Fujian”, and the World Horticultural Expo “Fujian Day”, as well as the “China in the New Era”. Fujian: “Eco-Fujian Silk Road Sailing”, the National Art Fund Farmer’s Lacquer Painting Exhibition in Japan (Tokyo and Okinawa), and the Fujian Non-Foreign Relics World Fujian Business Conference. Taking advantage of international events to disseminate Chinese culture and convey the concept of “seeing people, seeing things, seeing life” in the protection of non-legacy is an important path to “revitalize” non-legacy culture.
The DEMATEL-ISM method is an integrated application of Decision Laboratory Analysis (DEMATEL) and Interpretive Structural Modelling (ISM) [29].
DEMATEL is a systematic analytical method that is based on matrix and graph theory and can be utilized to tackle complex problems in reality [30]. The method is based on graph theory and matrix theory, based on the logical relationship between the elements, through the use of matrix calculation techniques, to obtain the degree of influence of each element on the other elements and the degree of influence, so as to calculate the degree of the centre of each element and the degree of cause. The advantage of this method lies in its quantitative analysis ability, which can transform the degree of influence and importance of each element in the system into specific numerical values so that the researcher can identify the key elements more clearly and then effectively simplify the complexity of the research problem. Meanwhile, due to its intuition, practicality, and convenience, the method has been widely used in many research fields, providing strong support for in-depth research and innovative practice in various fields.
The Interpretative Structural Modelling (ISM) method, which is essentially a systematic approach with a wide range of applications [31], lists the influencing factors to be examined and combines them with the actual correlation between the factors to obtain a directed graph. Subsequently, based on Boolean logic, the system structure that lacks clarity is further transformed into an ISM model. In general, the ISM method is used to determine the relationship between variables and their effects in various domains, and in order to obtain an operational model, it is necessary to apply a completely analytical approach and to generalise the existing experience. The significant advantage of this model is that it brings together multiple ideas held by scholars and makes the relationships clear to the public, so it is often used for both micro and macro issues.
The DEMATEL method is often used in the micro dimension to establish the strength of indirect and direct relationships between factors and to demonstrate the significance of the system-based approach. In general, the ISM model is often used in the macro-dimension, which can be used to analyse the role of the relationship between the various factors so as to make the overall structure of the system more and more simple. ISM and DEMATEL methods have their advantages and disadvantages, and they work together to make the analysis process more scientifically significant, which will play a significant complementary role in the results of the analysis. In addition, it can also moderately simplify the calculation steps, thus resulting in significant improvement in calculation efficiency.
This paper adopts the DEMATEL method to establish the influence matrix to obtain the corresponding comprehensive influence matrix, and as a basis for the construction of the overall relationship matrix, and then finally transformed into the ISM model of the required reachable matrix, and through the ISM method to divide the different levels of influence factors, and ultimately the formation of multi-layer hierarchical explanatory structure model. As shown in Figure 1.
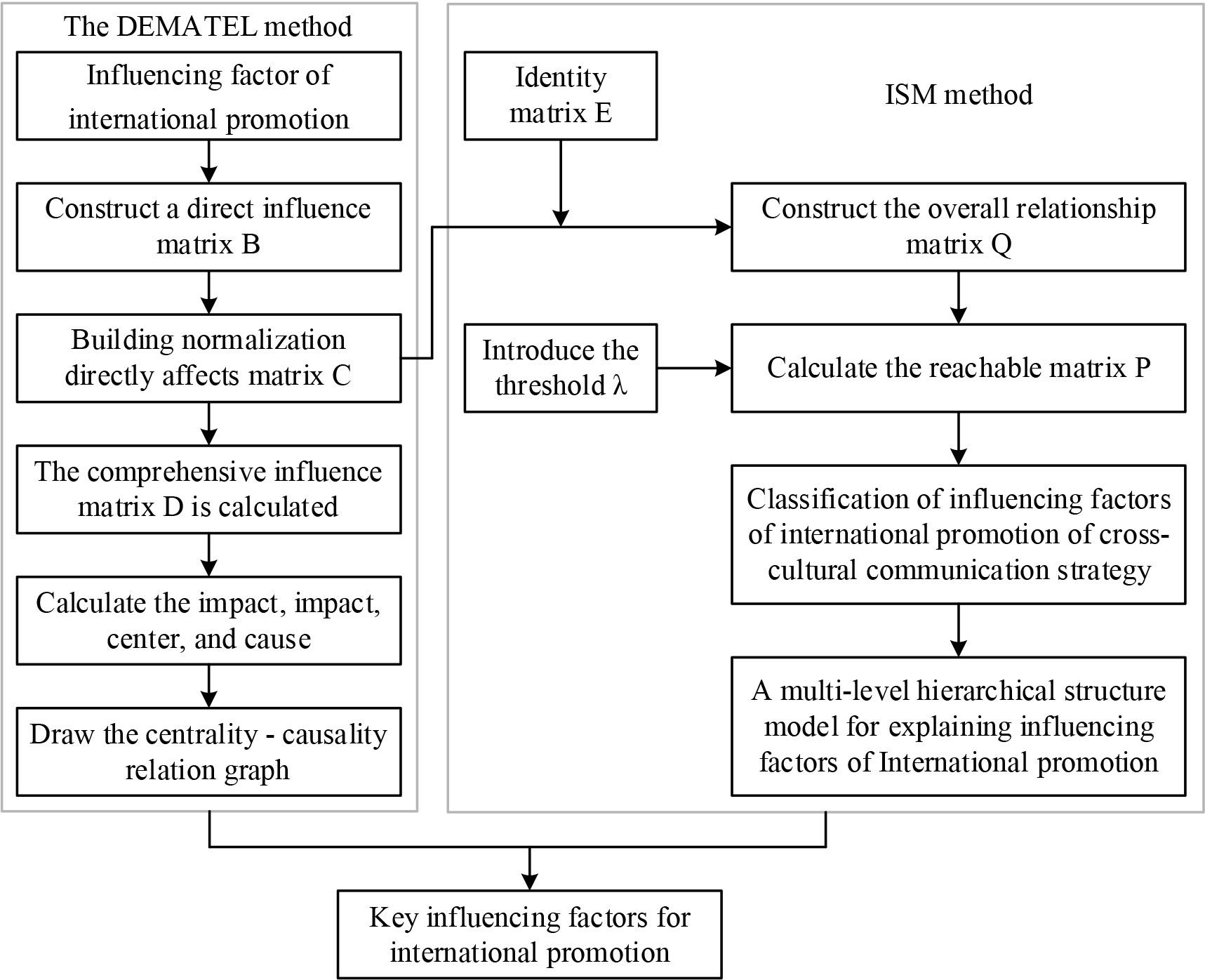
DEMATEL-ISM model construction process
The steps for calculating the main indicators of the DEMATEL-ISM model are as follows:
Step 1: Construct the direct impact matrix B. Determine the elements according to the object of analysis, set as H1, H2, ......, Hn. According to the relationship between different influencing factors of risk, use Step 2: Construct the normalised direct influence matrix C. The summing method is used to calculate all the elements of each row in the direct influence matrix and obtain the corresponding highest value, and the normalised direct influence matrix C is constructed according to formula (2):
Where Step 3: Calculate the integrated impact matrix D. The direct and indirect impacts are cumulated to construct the integrated impact matrix D according to the following equation. where E is the unit matrix due to Step 4: Calculate the degree of influence, the degree of being influenced, the degree of centrality and the degree of cause. The degree of influence is the sum of the values of the elements in each row of the matrix D, indicating the comprehensive influence on the other elements; the degree of influence is recorded as h. The degree of influence is the sum of the values of the elements in each column of the matrix D, indicating the comprehensive influence of the other elements. The degree of influence is recorded as e. The degree of influence and the degree of influence can be summed up to obtain the central degree of the centre of the central degree of the central degree of the degree of influence on behalf of the importance of the factor, the higher the value of the factor means the higher the degree of influence on the relevant factors and the higher the importance of the factor. The higher the value, the higher the influence of the influencing factor on the relevant factors and the greater the importance. The reason degree can be obtained by subtracting the influence degree from the influenced degree, and the reason degree is recorded as N. Factors with the reason degree >0 are the cause factors, and factors with the reason degree <0 are the effect factors. The formula (4) is as follows:
Step 5: Calculate the overall relationship matrix Q. Since the overall influence matrix D only deals with how each factor affects the other factors and not whether it affects itself, the unit matrix E is used to replace the influence on itself, and the unit matrix E is added to matrix D during the process of calculating the overall relationship matrix Q. Equation (5) is calculated as follows:
where E represents the unit matrix. Step 6: Calculate the reachability matrix P. The conversion from DEMATEL model to ISM model requires the introduction of a threshold The reachability matrix Step 7: Modelling the multilevel recursive order structure. After the reachable matrix P is calculated, the reachable set, the prior set and the intersection between them are determined according to the ISM method. Reachable set According to Equation (7), if there is
In order to select indicators that are systematic, scientific and sustainable, this paper has reviewed relevant literature and books on strategic promotion, cultural promotion and intercultural communication research and surveyed and visited people engaged in Fujian’s cultural sector, experts, teachers and relevant people who have participated in intercultural communication activities in Fujian Province in recent years. Thus, the first level of indicators of the international promotion factors of intercultural communication strategy in Fujian Province was initially constructed: governmental management factors, functional departmental factors, and other factors. On the basis of the preliminary construction of the first-level indicators, six second-level indicators and 15 third-level indicators of the indicator system of the influence factors of the international promotion of Fujian’s intercultural communication strategy were extended, and the specific contents of the indicator system are shown in Table 1.
Influencing factors of international promotion of Fujian cultural communication strategy
| Primary indicator | Secondary indicator | Tertiary indicator |
| Government management | Degree of importance | Policy support (X1) |
| Financial input (X2) | ||
| Implementation force (X3) | ||
| Resource allocation (X4) | ||
| Business development (X5) | ||
| Cross-cultural communication | Cultural communication (X6) | |
| Functional department | Development strategy | Promotion strategy (X7) |
| Communication media (X8) | ||
| Organization & management | Qualification management (X9) | |
| Job supervision (X10) | ||
| Other factors | Relevant personnel | Talent cultivation (X11) |
| Intangible heritage inheritors (X12) | ||
| Technical personnel (X13) | ||
| Translators & interpreters (X14) | ||
| International environment | International environment (X15) |
Based on the factors influencing the international promotion of Fujian’s intercultural communication strategy in Table 1, the questionnaire was made using a scale of 0 to 4, where 0 represents no influence, 1 represents low influence, 2 represents medium influence, 3 represents high influence, and 4 represents very high influence. The questionnaires were distributed to technicians, managers, supervisors, professors and lecturers engaged in research and teaching in the field of international promotion who are engaged in intercultural communication and international promotion industry. A total of 105 questionnaires were distributed and 89 valid questionnaires were recovered, with an 84.76% valid questionnaire recovery rate. The reliability test was carried out with the commercial software SPSS, and the test result showed that the Cronbach’s α value was 0.682, which was greater than 0.600 and the reliability test was qualified, so the data can be used to carry out the analysis of the factors influencing the international promotion of Fujian’s cross-cultural communication strategy. In order to eliminate the influence of experts’ subjectivity on the results of factor analysis as much as possible, this study takes the arithmetic mean of each expert’s rating of each influence factor as the value of the influence factor and thus constructs the direct influence matrix B as shown in Table 2.
Direct influence matrix B
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 | X13 | X14 | X15 | |
| X1 | 0.00 | 2.67 | 0.07 | 0.17 | 1.18 | 0.10 | 2.10 | 1.89 | 3.40 | 3.43 | 0.14 | 3.45 | 0.96 | 0.92 | 1.15 |
| X2 | 2.15 | 0.00 | 2.30 | 1.35 | 1.58 | 1.50 | 1.37 | 1.73 | 2.63 | 2.13 | 1.40 | 0.63 | 1.78 | 2.89 | 0.34 |
| X3 | 0.75 | 1.80 | 0.00 | 2.21 | 0.51 | 0.12 | 0.17 | 1.53 | 2.66 | 3.40 | 1.57 | 1.70 | 0.19 | 1.92 | 0.24 |
| X4 | 2.48 | 3.11 | 3.12 | 0.00 | 1.82 | 0.08 | 3.44 | 3.31 | 2.08 | 1.52 | 0.61 | 0.80 | 1.54 | 1.18 | 3.42 |
| X5 | 2.20 | 2.11 | 3.09 | 2.72 | 0.00 | 3.19 | 0.14 | 2.70 | 2.51 | 2.63 | 0.73 | 0.00 | 2.04 | 0.24 | 1.23 |
| X6 | 2.85 | 1.26 | 1.04 | 0.05 | 2.05 | 0.00 | 3.29 | 3.24 | 3.20 | 3.16 | 3.27 | 2.39 | 2.30 | 0.74 | 0.01 |
| X7 | 2.12 | 0.33 | 0.42 | 2.11 | 2.96 | 0.90 | 0.00 | 0.19 | 0.22 | 1.47 | 2.09 | 2.24 | 0.31 | 3.17 | 0.16 |
| X8 | 2.47 | 1.33 | 1.02 | 2.25 | 1.87 | 2.23 | 2.98 | 0.00 | 0.36 | 2.45 | 1.07 | 0.24 | 1.18 | 2.59 | 1.76 |
| X9 | 2.65 | 0.78 | 0.60 | 3.27 | 0.11 | 1.59 | 1.06 | 1.68 | 0.00 | 2.37 | 2.70 | 2.75 | 2.64 | 0.18 | 1.14 |
| X10 | 3.12 | 1.39 | 2.11 | 0.57 | 0.73 | 1.46 | 1.57 | 2.55 | 0.20 | 0.00 | 2.99 | 0.33 | 3.06 | 0.28 | 0.44 |
| X11 | 2.28 | 0.81 | 3.44 | 3.27 | 0.67 | 0.94 | 1.18 | 0.01 | 1.30 | 2.51 | 0.00 | 0.80 | 1.29 | 0.81 | 0.47 |
| X12 | 0.84 | 1.49 | 1.87 | 3.20 | 2.84 | 0.78 | 3.14 | 0.21 | 2.84 | 0.38 | 2.14 | 0.00 | 0.63 | 1.94 | 0.42 |
| X13 | 1.16 | 1.66 | 0.76 | 0.18 | 3.23 | 0.27 | 1.45 | 0.02 | 2.21 | 3.31 | 0.03 | 2.20 | 0.00 | 1.51 | 1.11 |
| X14 | 3.15 | 2.16 | 0.02 | 3.09 | 3.35 | 1.94 | 0.42 | 1.14 | 1.45 | 2.03 | 2.40 | 3.00 | 1.60 | 0.00 | 0.14 |
| X15 | 1.93 | 2.56 | 0.25 | 1.55 | 1.99 | 2.26 | 1.30 | 2.44 | 3.41 | 0.45 | 0.28 | 3.41 | 3.40 | 0.84 | 0.00 |
According to the direct influence matrix B, in accordance with the construction steps of the DEMATEL coupled ISM integrated model, using MATLAB software to calculate, you can obtain the integrated influence matrix D, as shown in Table 3.
Comprehensive influence matrix D
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 | X13 | X14 | X15 | |
| X1 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.21 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.03 |
| X2 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.26 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.02 |
| X3 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.01 |
| X4 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.07 |
| X5 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.01 |
| X6 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| X7 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.09 |
| X8 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| X9 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| X10 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.01 |
| X11 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| X12 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.05 |
| X13 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| X14 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.00 |
| X15 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
In the DEMATTEL methodology, Influence D value, Influenced C value, Centrality (D+C) value, and Causality (D-C) value are used to assess the relative importance of the factors or variables and their interrelationships, which contribute to a better understanding and solution of the research problem. Based on the above concepts, this study identifies the factors influencing the international promotion of Fujian’s intercultural communication strategy based on the numerical calculation and comprehensive ranking of four key indicators, including the D value of Influence Degree, the C value of Influenced Degree, the Centrality Degree (D+C) value, and the Causality Degree (D-C) value, and the specific results are shown in Table 4.
DEMATEL calculation index value
| Influence degree (D) | Influenced degree (C) | Center degree (D+C) | Center degree rank | Reason degree (D-C) | Factor attribute | |
| X1 | 1.32 | 0.17 | 1.49 | 6 | 1.15 | Reason |
| X2 | 1.51 | 0.18 | 1.69 | 4 | 1.33 | Reason |
| X3 | 0.84 | 0.26 | 1.10 | 10 | 0.58 | Reason |
| X4 | 0.73 | 0.24 | 0.97 | 11 | 0.49 | Reason |
| X5 | 0.54 | 0.38 | 0.92 | 13 | 0.16 | Reason |
| X6 | 0.42 | 1.00 | 1.42 | 7 | -0.58 | Result |
| X7 | 0.97 | 0.55 | 1.52 | 5 | 0.42 | Reason |
| X8 | 0.52 | 0.63 | 1.15 | 9 | -0.11 | Reason |
| X9 | 0.42 | 0.96 | 1.38 | 8 | -0.54 | Result |
| X10 | 0.56 | 1.18 | 1.74 | 3 | -0.62 | Result |
| X11 | 0.42 | 1.39 | 1.81 | 1 | -0.97 | Result |
| X12 | 0.48 | 1.28 | 1.76 | 2 | -0.80 | Result |
| X13 | 0.11 | 0.39 | 0.50 | 15 | -0.28 | Result |
| X14 | 0.29 | 0.64 | 0.93 | 12 | -0.35 | Result |
| X15 | 0.48 | 0.36 | 0.84 | 14 | 0.12 | Reason |
Centrality indicates the importance of a factor in influencing the development of international promotion of intercultural communication strategies in Fujian. The larger the centrality, the more important the factor is. The degree of cause is the indication of how a factor affects other factors, and if it is greater than 0 it is the cause factor, while if it is less than 0 it is the resulting factor. Table 4 shows that the top three factors in the centrality degree are X11, X12, and X10, indicating that these three factors are relatively important factors affecting the international promotion of Fujian’s intercultural communication strategy. The cause factors include X1, X2, X3, X4, X5, X7, X8, and X15, and the top-ranked factors are the key factors affecting the international promotion of Fujian’s intercultural communication strategy. The result factors include X6, X9, X10, X11, X12, X13, and X14, and the top-ranked factors indicate that they are vulnerable to the influence of the cause factors, which in turn affects the development of international promotion of Fujian’s intercultural communication strategy.
Based on the data obtained from the integrated influence matrix D, the appropriate threshold λ is determined, and the adjacency matrix is constructed. Table 5 displays the reachability matrix R obtained through the Boolean matrix algorithm.
Accessibility matrix R
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 | X13 | X14 | X15 | |
| X1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| X2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| X3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| X4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| X5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| X6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| X7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| X8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| X9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| X10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| X11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| X12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| X13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| X14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| X15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
The reachable set K(Xi), the precedence set Z(Xi), and the intersection set N(Xi) are derived based on the reachable matrix R. K(Yi) denotes that the factor Xi can influence the other factors in the system, and Z(Xi) denotes that the other factors influence Xi. The highest level factor set L1 of the matrix can be obtained when K (Xi) ∩Z (Xi) =K (Xi). Then, the rows and columns corresponding to each influential factor in L1 are deleted from the reachable matrix R to obtain a new matrix, and the same operation is performed until all influential factors are extracted and divided into different levels. The final stratification results are L1={11, 12, 13, 14}, L2={9, 10}, L3={6, 7, 8}, L4={3, 4, 5, 15}, L5={1, 2}. According to the results of the hierarchical division, a hierarchical structure diagram of factors influencing the promotion of energy-saving renovation of existing buildings is constructed, as shown in Figure 1. From Figure 1, it can be seen that the international promotion of Fujian’s cross-cultural communication strategy influences factors.
X1 (policy support) and X2 (financial input) in Level 5 are deep causal factors that can indirectly affect the international promotion of Fujian’s intercultural communication strategy by influencing other factors and should be highly valued.
In Level 1, X11 (talent training), X12 (non-genetic inheritors), X13 (technicians), and X14 (interpreters) are superficial causal factors that are the direct influences on the international promotion of Fujian’s intercultural communication strategy. Increased cultivation of talents and improved quantity and quality of technicians and interpreters will help the main actors have a better understanding of Fujian’s culture. The non-heritage bearers, on the other hand, are conducive to the display of diversified Fujian culture, enriching the content of cross-cultural communication.
The factors in Tier 2 - Tier 4 are transitional causal factors. The existence of transitional causal factors can induce the emergence of surface causal factors. There is a pair of strong correlation factors, X4 (resource allocation) and X5 (business development). Resource allocation efficiency is closely related to business development in cross-cultural communication, and efficient resource allocation can help Fujian gain more business benefits in the process of cross-cultural communication.
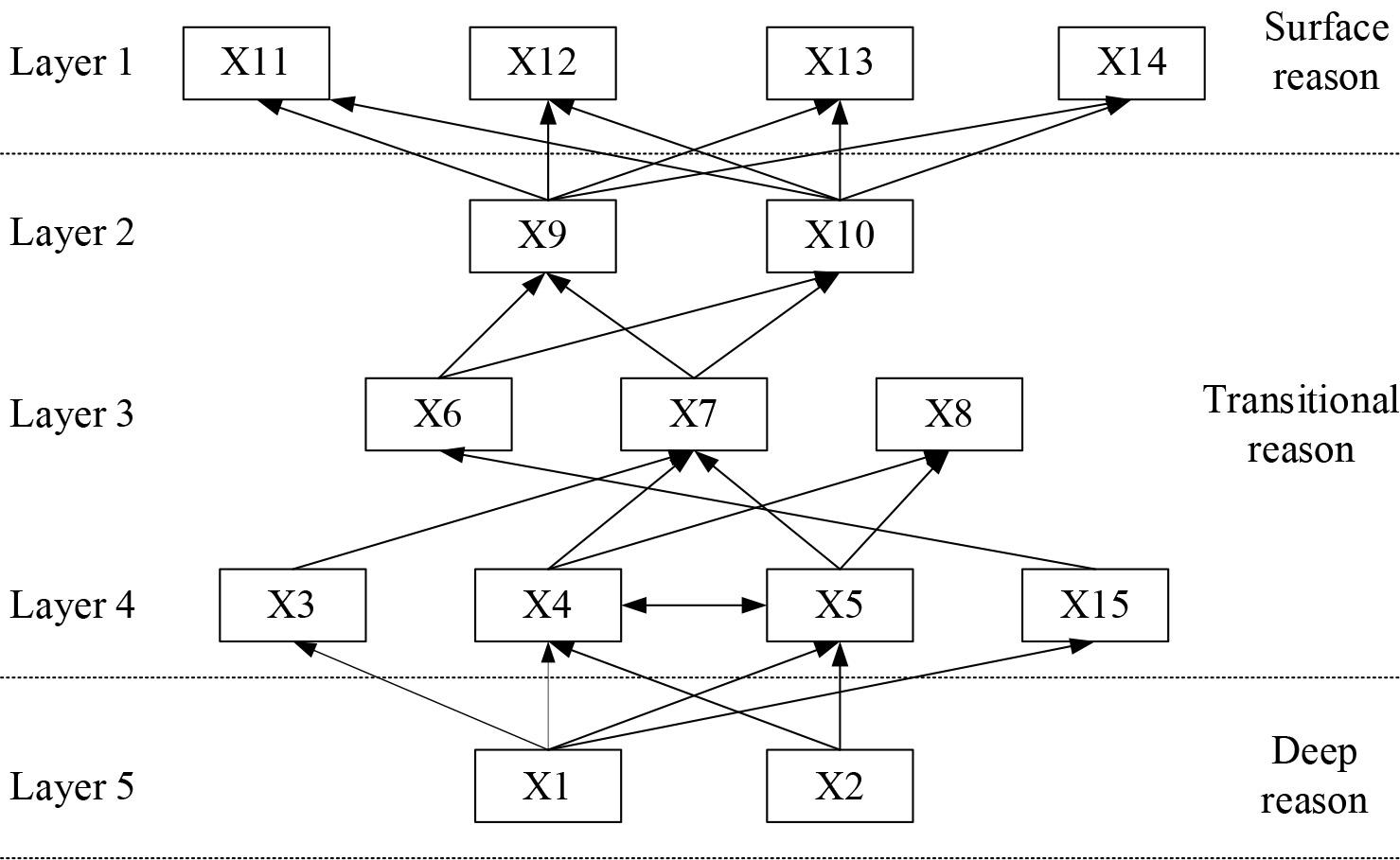
Hierarchical structure of influencing factors of international promotion
Tapping Talents Deeply to Achieve Efficient International Promotion of Intercultural Strategies
Through the above empirical analyses, it can be seen that factors such as talent cultivation and non-genetic inheritance play an important role, which reflects the importance of local and national cultures in cross-cultural communication. In order to meet the demand, Fujian Province can cooperate with local universities and formulate relevant policies for talent introduction to meet the talent demand for international promotion of cross-cultural strategies.
Improve the promotion strategy of intercultural communication strategy to ensure the efficiency and stability of the strategy.
The communication media and promotion strategies of international promotion play a key role in the international promotion of Fujian’s intercultural strategy, which indicates that effective communication media and promotion strategies are the key to ensuring the wide coverage and deep participation of Fujian’s intercultural strategy. It is recommended that Fujian should consider various promotional channels and methods, such as online social media, mobile applications, and offline activities, to ensure that the promotional message reaches various groups and regions. Strengthening media promotion efforts, such as extensive publicity through partners, social media, and traditional media, is also key to improving the effectiveness of intercultural communication strategy promotion.
Increase policy support and financial support to promote high-quality promotion of intercultural strategies
Policy support and financial input are key factors in promoting intercultural strategies internationally in Fujian. Greater policy support means that the implementation of the international promotion of intercultural strategies will be accelerated, and financial allocations will be used to build more convenient promotion platforms, lay out wider dissemination areas, and increase the radius of Fujian’s intercultural communication strategies.
The article conducts a preliminary study on Fujian’s intercultural communication strategy, introduces the DEMATEL-ISM model to explore the factors influencing the international promotion of Fujian’s intercultural communication strategy, and then proposes corresponding international promotion strategies based on the results.
Among the factors influencing the international promotion of Fujian’s intercultural communication strategy, X11 (talent cultivation), X12 (non-genetic inheritance), and X10 (work supervision) ranked the top three in terms of centrality, with the centrality of 1.81, 1.76, and 1.74 respectively, which are relatively important factors affecting the international promotion of Fujian’s intercultural communication strategy. Financial Input), X3 (Implementation Effort), X4 (Resource Allocation), X5 (Business Development), X7 (Promotion Strategy), X8 (Communication Media), and X15 (International Environment) belong to the cause factors, while X6 (Cultural Communication), X9 (Eligibility Management), X10 (Work Supervision), X11 (Talent Cultivation), X12 (Non-Genetic Inheritance), X13 (Technicians), and X14 ( Interpreter) belong to the outcome factors. Among all the influencing factors, X1 and X2 belong to deep causative factors, X3~X10 and X15 belong to transitional causative factors, and X11~X14 are surface causative factors.
Fujian Social Science Fund Project: Research on Fujian’s International Communication Strategy Based on the Belt and Road Initiative (Project No.: FJ2024BF033).
